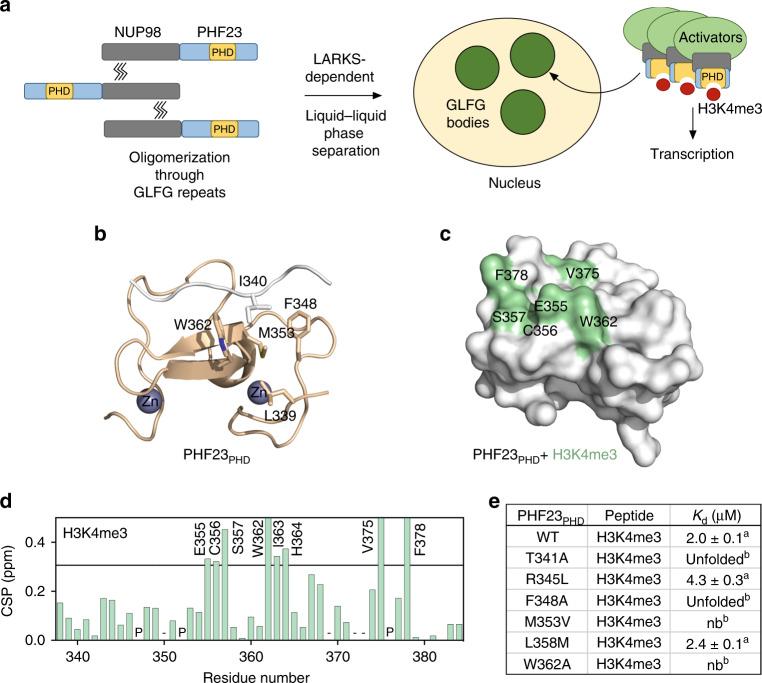
Fig. 2. Molecular basis for the recognition of H3K4me3 by PHF23PHD.
a A model for the leukemic activity of the NUP98–PHF23 fusion. b Structure of PHF23PHD. The N-terminus of another PHF23PHD molecule (white) binds in the histone-binding site of the domain. The side chain of I340 occupies the aromatic cage. Source data are provided in the Source Data file. c, d Identification of the H3K4me3-binding site of PHF23PHD. Residues that exhibit H3K4me3-induced resonance changes in (d) are mapped onto the structure of PHF23PHD in (c). Histogram shows NMR chemical shift perturbations in PHF23PHD upon binding of H3K4me3 peptide at a 1:4 ratio. ‘P’ indicates a proline residue. ‘−’ indicates an unassigned residue. Bars reaching the maximum of y-axis indicate disappeared cross-peaks. Source data are provided in the Source Data file. e Binding affinities of the PHF23PHD mutants to the H3K4me3 peptide as measured by tryptophan fluorescence (a) or by NMR titration experiments (b).