Fig. 1. Whisker somatosensory thalamic nuclei and their cortical projections revealed through AAV-mediated anterograde trans-synaptic gene expression.
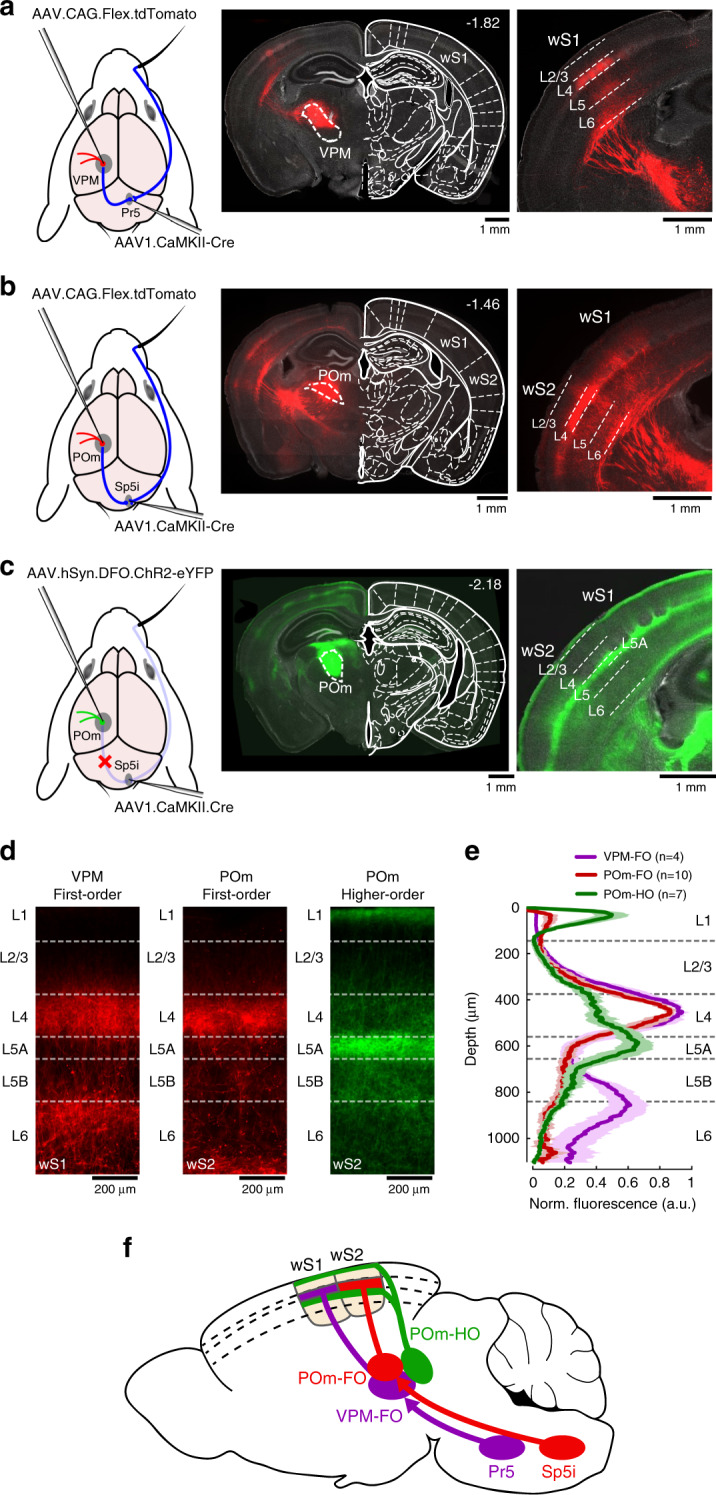
a AAV1 viral vector was injected in Pr5 of the brainstem to express Cre-recombinase in a trans-synaptic anterograde manner. A second AAV injection in the thalamus expressing a Cre-dependent tdTomato fluorescent protein resulted in labeling of VPM neurons receiving direct inputs from Pr5. Left: schematic of the injection protocol. Middle: Example coronal section with VPM neurons expressing tdTomato in comparison to a reference atlas22 (distance from bregma indicated). Right: Axonal innervation of VPM neurons in wS1. This experiment was repeated in four mice with similar results. b Same as a, but for POm neurons receiving direct inputs from Sp5i. This experiment was repeated in ten mice with similar results. c Same as b, but for POm neurons not expressing Cre-recombinase through trans-synaptic transfection from Sp5i injections. Here, the second viral vector injected in the thalamus only allowed expression of eYFP conditionally on the absence of Cre-recombinase. This experiment was repeated in seven mice with similar results. d Examples of laminar-specific axonal innervation in somatosensory cortices originating from different thalamic nuclei. e Normalized fluorescent expression profile averaged over mice (n = 4 mice for VPM first-order (VPM-FO), n = 10 mice for POm first-order (POm-FO), n = 7 mice for POm higher-order (POm-HO)). Shaded areas: s.e.m. f Schematic of the different somatosensory thalamocortical circuits. The schematic drawings of the brain in panels a–c are reproduced from Paxinos and Franklin (2001) with permission from Elsevier.
