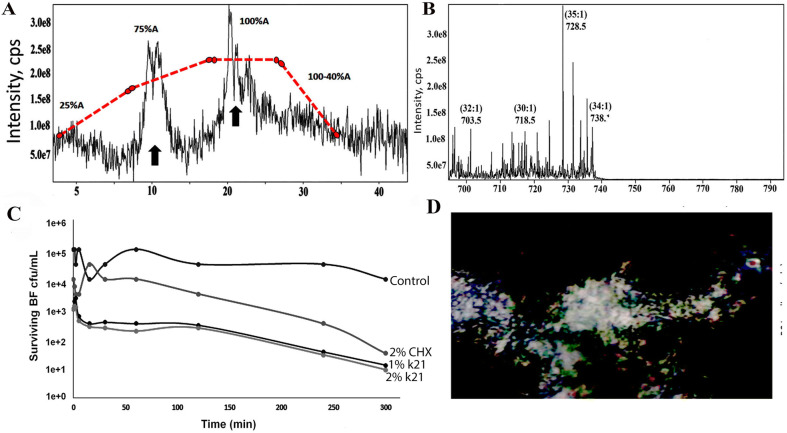
Figure 6.
(A) Tandem mass spectroscopy analysis of extracted membrane lipids showing effective separation of membrane lipids based on hydrophobicity with the different elution time points. Extracted dual species bacterial organism’s membrane lipids with dotted lines indicated the change in gradient and concentration as QAS percentage was increased to 2% with typical elution time for membrane phospholipids of Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus acidophilus biofilm. (B) Tandem mass spectroscopy scan showing different ion modes indicating fragmentation of this species to yield different fatty acyl chains in 1% QAS molecules. (C) Time–kill curves of dual specie biofilms treated with different concentrations of antimicrobials. The surviving bacteria were plated at various time points (0–300 min). Both 1% QAS and 2% QAS were able to retard growth for 300 min even after washing during the time-kill assay. After 1 min of QAS treatment, bacterial cells were reduced and showed less survivability. (D) Confocal intensity of area of biofilm in 1% QAS specimens under consideration with excitation performed at λ = 514 nM; QAS quaternary ammonium silane, CHX chlorhexidine, BF biofilm, cps count per second.