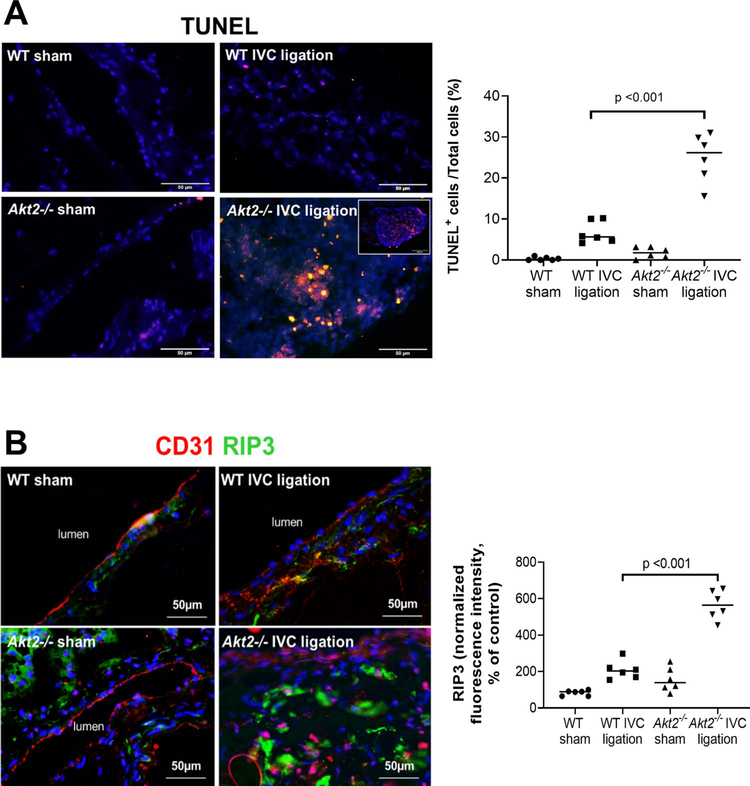
Fig. 3.
Significantly increased cell death in the ligated inferior vena cava (IVC) of Akt2−/− mice. Wild-type (WT) mice and Akt2−/− mice underwent a sham operation or IVC ligation. The thrombus-containing IVC was harvested at 2 weeks after ligation. a Representative images of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining and quantification showing that apoptosis was significantly increased in the lesion areas of the ligated IVC of Akt2−/− mice, particularly in thrombus areas. For the quantification of staining, the number of TUNEL-positive cells was normalized to the total number of cells evaluated. All values represent the mean (n = 6 in each group). P-values were obtained by performing one-way ANOVA analysis followed by the Holm-Sidak multiple comparisons test. b Representative images of immunofluorescence staining and quantification showing a significant increase in the levels of the necroptosis molecule receptor-interacting protein kinase 3 (RIP3) in the ligated IVC of Akt2−/− mice. For the quantification of staining, the mean positive-staining area was normalized with the evaluated aortic area. All values represent the mean (n = 6 per group). P-values were obtained by performing one-way ANOVA analysis followed by the Tukey multiple comparisons test