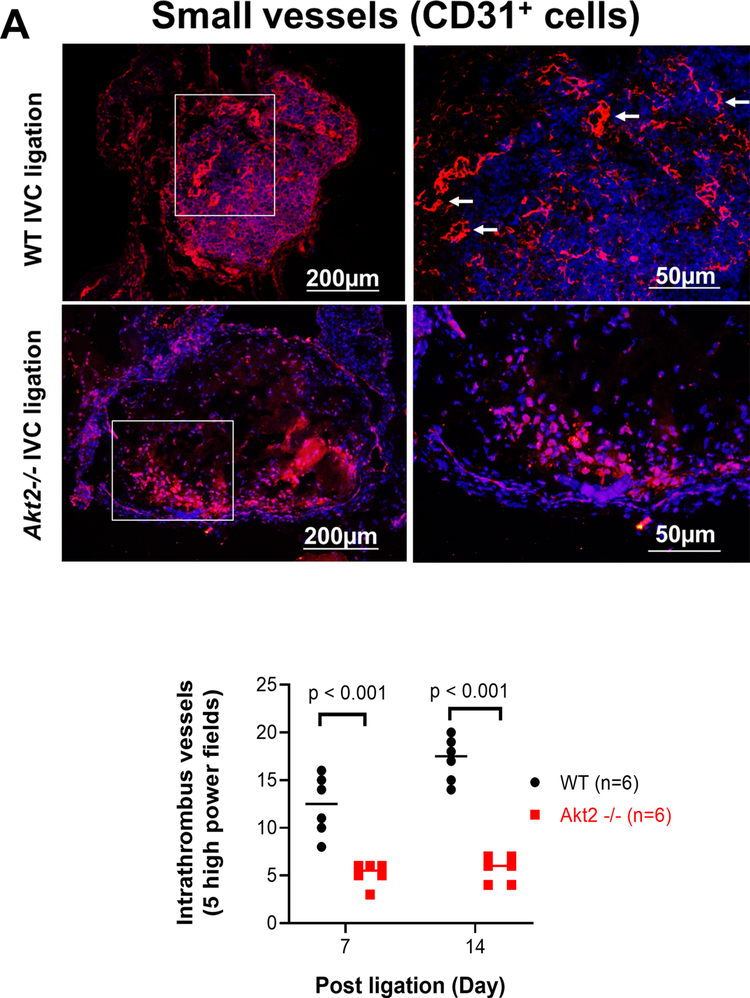
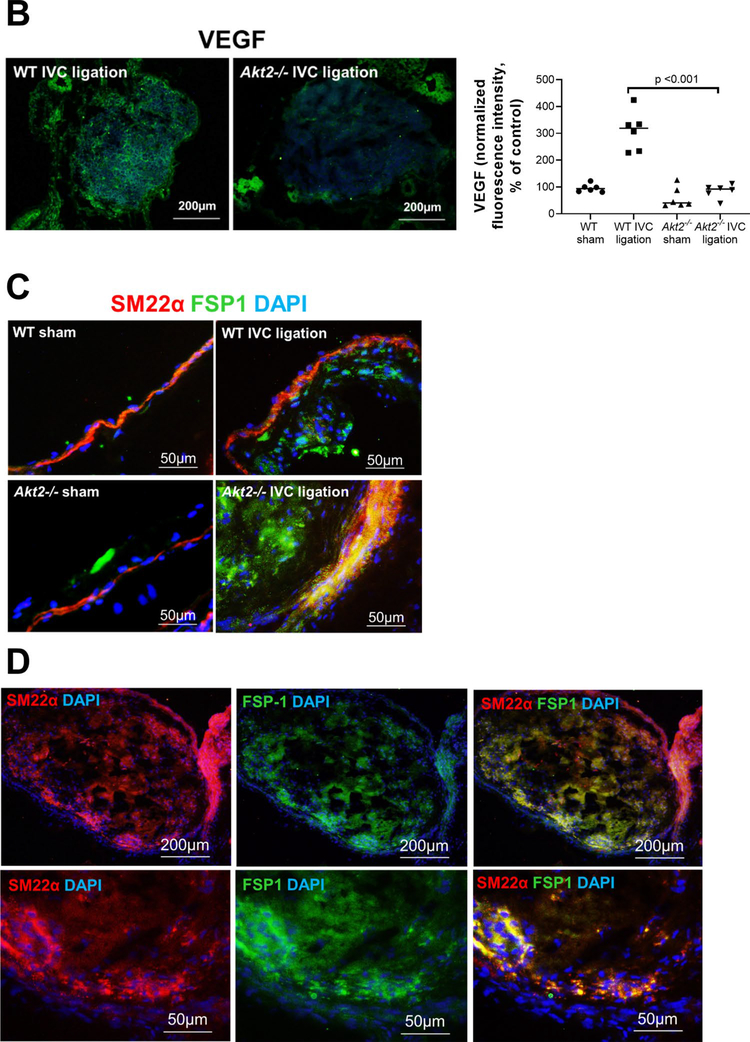
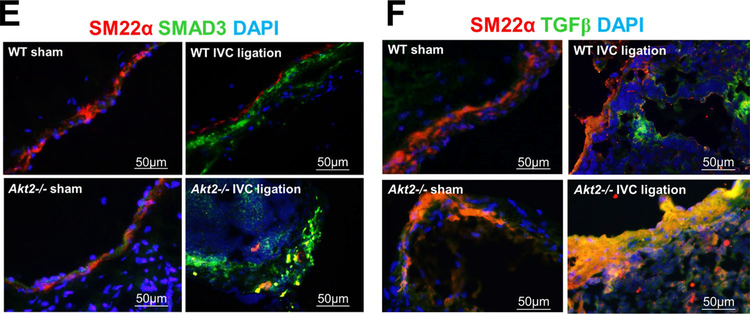
Fig. 4.
Impaired intrathrombotic angiogenesis and recanalization and increased fibrotic remodeling in the ligated inferior vena cava (IVC) of Akt2−/− mice. Wild-type (WT) mice and Akt2−/− mice underwent a sham operation or IVC ligation. The thrombus-containing IVC was harvested at 2 weeks after ligation. a The IVC from WT or Akt2–/– mice was stained with endothelial marker CD31. Intrathrombotic CD31-positive neovessels with tube-like formation were counted in 5 high-magnification fields (× 400). Representative images of staining and quantification of the number of neovessels showing a significantly decreased number of neovessels in the ligated IVC of Akt2−/− mice. All values represent the mean (n = 6 per group). P-values were obtained by performing one-way ANOVA analysis followed by the Tukey multiple comparisons test. b Representative images of immunofluorescence staining and quantification showing decreased vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in the ligated IVC of Akt2−/− mice. For the quantification of staining, the mean positive-staining area was normalized with the evaluated IVC area. All values represent the mean (n = 6 per group). P-values were obtained by performing multiple comparisons in one-way ANOVA analysis followed by the Tukey multiple comparisons test. c Representative images of immunofluorescence staining showing fibroblast specific protein (FSP)-1–positive cells in the ligated IVC of WT mice, which were even more abundant in the ligated IVC of Akt2−/− mice. d Representative images of double immunofluorescence staining showing the colocalization of FSP-1 with the smooth muscle cell marker SM22-α in the vein wall and in the thrombus of ligated IVC in Akt2−/− mice. e, f Representative images of immunofluorescence staining showing increased levels of e SMAD3 and f TGF-β in the ligated IVC of Akt2−/− mice compared with WT mice