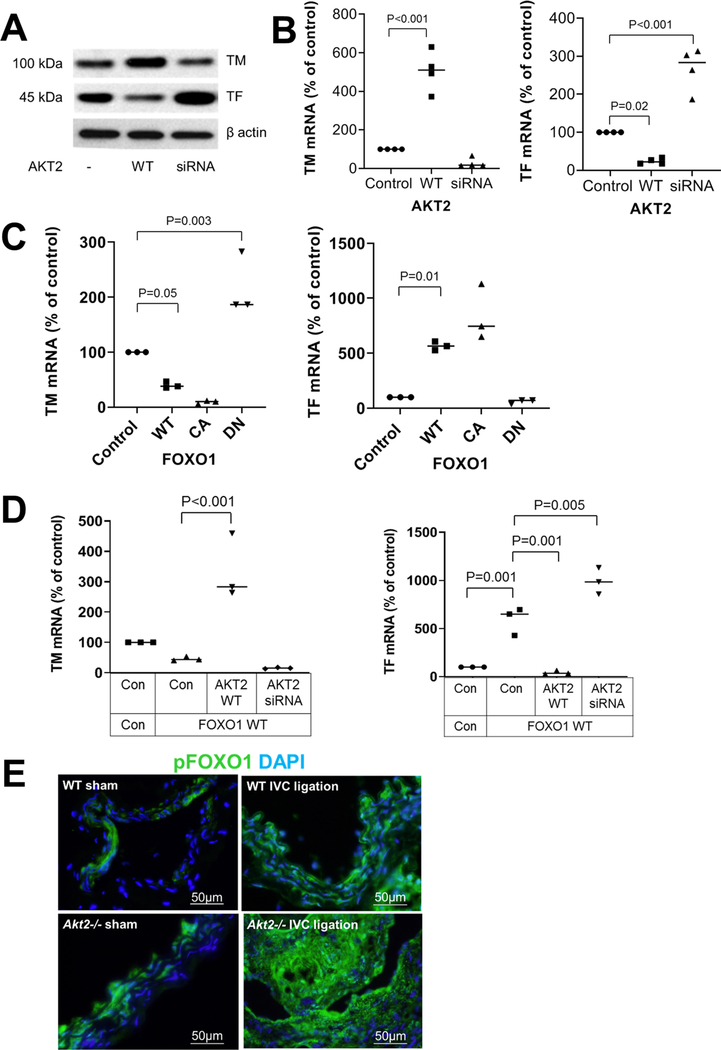
Fig. 5.
Inhibition of the FOXO1-mediated regulation of thrombomodulin (TM) and tissue factor (TF) expression by AKT2. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) were transfected with wild-type (WT)-AKT2 or AKT2 siRNA. Western blot analysis a and results of quantitative RT-PCR b showing a trend of induced TM expression and reduced TF expression by AKT2 overexpression. mRNA levels were normalized with those of β-actin and are expressed as the percentage of the control. Data represent the mean of 3 biologic repeats. c HUVECs were transfected with plasmids expressing WT-FOXO1, constitutively active (CA)-FOXO1, or dominant negative (DN)-FOXO1. Quantitative RT-PCR results showing that WT-FOXO1 and CA-FOXO1 induced a trend of reduced TM expression and induced TF expression. DN-FOXO1 had opposite effects. mRNA levels were normalized with those of β-actin and are expressed as the percentage of the control. Data represent the mean of 3 biologic repeats. d HUVECs were transfected with WT-FOXO1 plasmid in the presence of WT-AKT2 and AKT2 siRNA. Quantitative RT-PCR results showing that AKT2 reversed the FOXO1-mediated inhibition of TM and stimulation of TF. The relative levels of mRNA are expressed as the percentage of the control. Data represent the mean of > 3 biologic repeats. P-values were obtained by performing multiple comparisons in one-way ANOVA analysis followed by the Tukey multiple comparisons test. e Wild-type (WT) mice and Akt2−/− mice underwent a sham operation or IVC ligation. The thrombus-containing IVC was harvested at 2 weeks after ligation. Representative images of immunofluorescence staining showing increased phospho FOXO1 (p-FOXO1) levels in the ligated IVC of Akt2−/− mice compared with WT mice