Fig. 4.
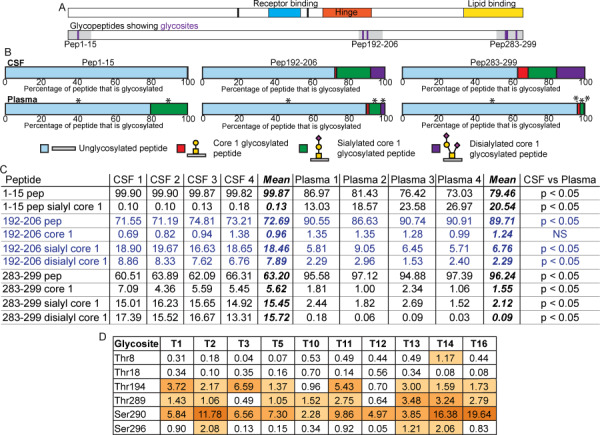
Comparison of the glycoprofiles of CSF and plasma APOE. (A) Schematic of APOE domain structures showing amino acids 112 and 158 in black, the receptor-binding domain in blue, the hinge in orange and the lipid-binding domain in yellow. The schematic below shows glycosylated tryptic peptides in grey with position of glycosites in purple. (B) Average percentage of identified peptide that was unglycosylated (pale blue), glycosylated with Galβ1–3GalNAcα1- (red), Neu5Acα2–3Galβ1–3GalNAcα1- (green) or Neu5Acα2–3Galβ1–3(Neu5Acα2–6)GalNAcα1- (purple) from CSF (n = 4, top) and plasma (n = 4, bottom) samples. Asterisks (*) above the plasma bars designates peptides that showed a statistically significant difference between the CSF and plasma samples where the P value was less than 0.05 as determined by a Mann–Whitney nonparametric test. P values were FDR adjusted to correct for multiple comparisons. (C) Relative quantitative data and statistics for individual CSF and plasma samples shown in (B). All data are shown as percentages, and the mean follows the four CSF and four plasma samples. As described above, Mann–Whitney non-parametric tests were performed to compare the results obtained for each peptide from the CSF and plasma samples. P values were FDR-adjusted to correct for multiple comparisons. These P value results are shown at the end of the table with significance designated as a P value of less than 0.05. Blue text is used only to delineate peptides for ease of reading. (D) ISOGlyP results for APOE glycosites. T refers to the individual GalNAc-T. Results are shown as EVP (enhancement value product) which refers to the preference a GalNAc-T shows towards glycosylating a glycosite: greater than 1 correlates with a positive likelihood of that glycosite being able to be glycosylated by that GalNAc-T, and less than 1 suggests a negative correlation with that specific GalNAc-T. The EVP does not correlate with the probability of that glycosite being glycosylated. ISOGlyP results are GalNAc-T-specific as it only considers 10 of the 20 known enzymes; others may contribute to glycosylation at any particular glycosite.
