Figure 1.
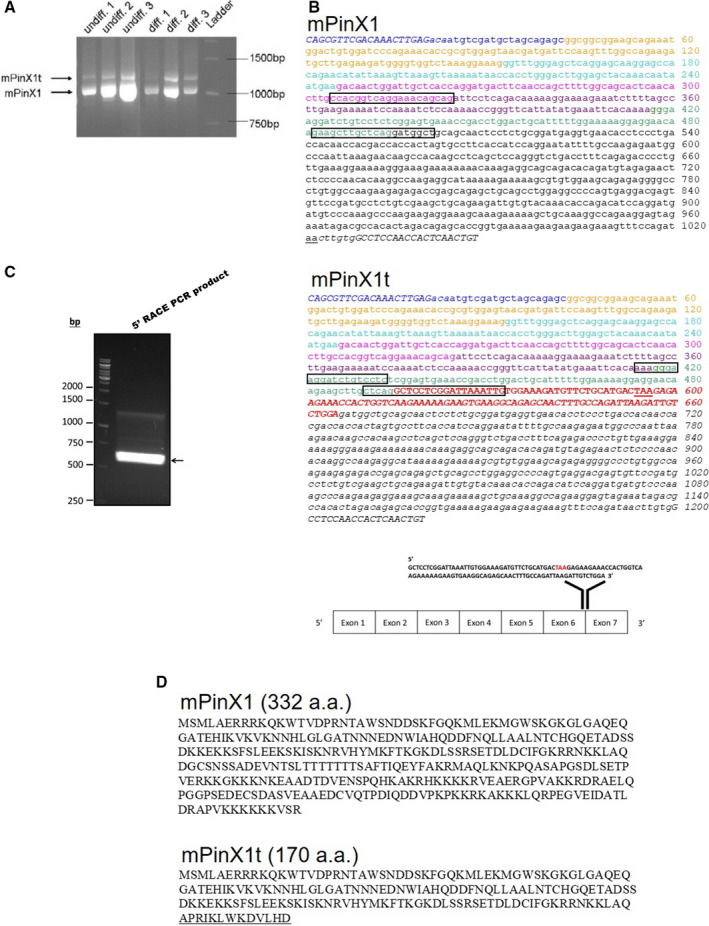
Discovery of mPinX1t, the novel transcript variant of mPinX1. A, Presence of 2 splice variants, mPinX1 and mPinX1t, as revealed by RT‐PCR. In the PCR, primers flanking the coding sequence of mPinX1 were used. Two splice variants were detected in both undifferentiated mESCs (undiff) and their differentiation derivatives (diff). B, cDNA sequences of (upper panel) mPinX1 and (middle panel) mPinX1t. Different colors represent different exons. Note that there is an extra exon in mPinX1t as represented by red and bold nucleotides. Start codon and stop codon are underlined. Italic nucleotides represent nucleotides at the untranslated regions. Italic and bold nucleotides located at the beginning and the end of the sequences represent PCR primer sequences used in (A). Boxed regions indicate the location of primers used in qPCR reactions. (Lower panel) Extra 111 nucleotides of mPinX1t was found to locate between exon 6 and exon 7 of mPinX1 sequence. Stop codon “TAA” is highlighted in red. C, Result of 5′RACE PCR reaction using primer specific for the 5′ added sequence and primer complementary to the mPinX1t sequence. The result indicated the presence of mPinX1t mRNA with intact 5′UTR. D, Amino acid sequence of (upper panel) mPinX1 and (lower panel) mPinX1t. mPinX1t contains the N‐terminal of mPinX1 (1–157 amino acids) but lacks the C‐terminal of mPinX1. Amino acids that are underlined represent the sequence that is present only in mPinX1t. 5′RACE indicates 5′ rapid amplification of cDNA ends; 5′UTR, 5′ untranslated region; mESCs, mouse embryonic stem cells; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; RT‐PCR, reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.
