Figure 1.
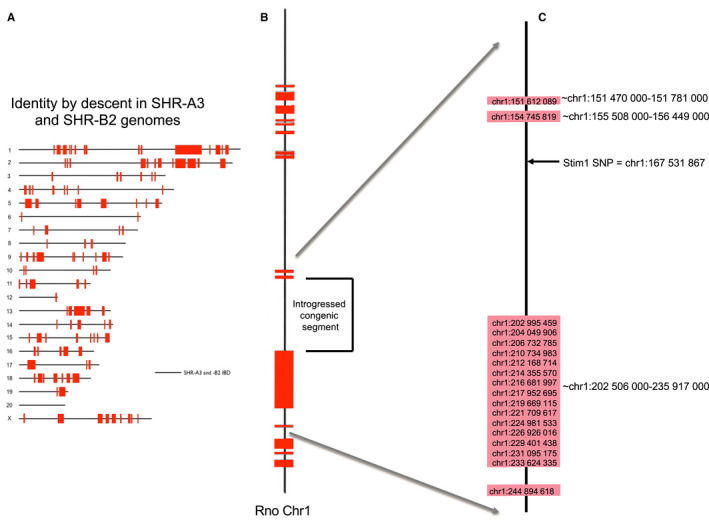
Chromosome scale view of congenic transfer of an identical‐by‐descent (IBD) haploblock containing wild‐type Stim1 from SHR‐B2 in the SHR‐A3 genetic background. A, Regions of genetic IBD sequences are shown for the SHR‐A3 and SHR‐B2 genomes (20 autosomes and X chromosome. This block was initially identified by genotyping ≈10 000 genome‐wide SNPs. It has been confirmed, and its boundaries precisely defined, by whole‐genome sequencing. All SHR lines are the progeny of a single progenitor male and therefore lack ancestral Y chromosome variation). Red blocks indicate regions of the genome at which the 2 rat lines are descended from different ancestors. Solid black lines represent the remaining 87% of the genome that is IBD. B, Enlarged view of the rat chromosome 1 (Rno chr1) indicating the target haplotype block transferred from SHR‐B2 into the SHR‐A3 background. C, Detailed view of the approximate beginning and end points of the haplotype blocks surrounding the transferred segment (indicated to the right of the blocks and determined by examination of whole‐genome sequence alignments of SHR‐A3 and SHR‐B2). The genomic position of single‐nucleotide polymorphisms in this region that were genotyped in speed congenic construction are indicated above the colored blocks. Inheritance of the Stim1 wild‐type allele was determined by PCR amplification of the sequence including the polymorphic site. Stim1 genotype was determined by restriction digestion of the PCR products with AluI, which digests the SHR‐A3 mutated sequence but not the wild‐type SHR‐B2 sequence. PCR indicates polymerase chain reaction; SHR, spontaneously hypertensive rat; SNP, single‐nucleotide polymorphism.
