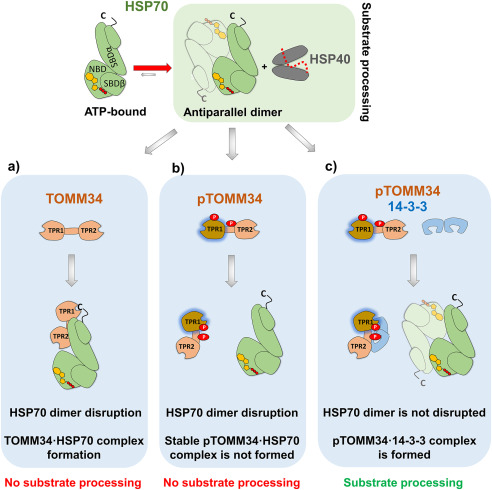
Figure 10.
TOMM34 interaction with HSP70 dimers is regulated by its PKA-mediated phosphorylation and 14-3-3 binding. ATP-bound HSP70 antiparallel dimers cooperate with HSP40 during protein substrate (dotted red line) processing (24). a, nonphosphorylated TOMM34 stably interacts with HSP70 in the ATP-bound state through TPR1-EEVD (c) contacts and an interface encompassing the TOMM34 interdomain linker (21, 24). This interaction leads to HSP70 dimer disruption, preventing substrate processing. b, PKA mediates TOMM34 phosphorylation (pTOMM34) on Ser93 and Ser160 residues (red circles), leading to structural loosening of the TPR1 domain and perturbation of the interaction interface formed between the TOMM34 interdomain linker and HSP70. pTOMM34 transiently interacts with HSP70, disrupting its dimeric structure and substrate processing activity, but a stable pTOMM34·HSP70 complex is not formed. c, 14-3-3 binding to pTOMM34 sequesters TOMM34 from HSP70 dimers leaving their substrate processing activity intact.