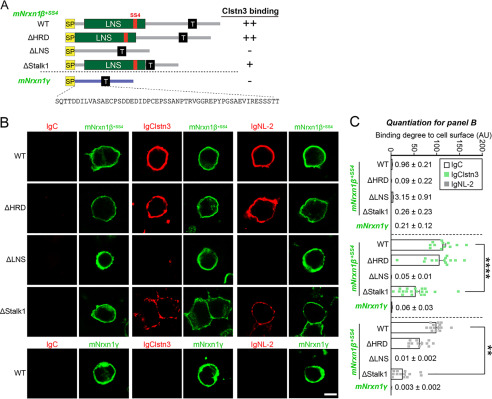
Figure 3.
Clstn3 binds to LNS domain of β-Nrxns. A, diagrams of Nrxn1β and Nrxn1γ constructs used in B. B, cell surface-binding assays. HEK293T cells expressing FLAG-tagged Nrxn1β+SS4 WT, its deletion variants (ΔHRD, ΔLNS, or ΔStalk1), or FLAG-tagged Nrxn1γ WT were incubated with IgClstn3, IgNL-2, or IgC, and analyzed by immunofluorescence imaging for Ig-fusion proteins (red) and FLAG (green). All binding reactions were performed in 2 mm CaCl2 and 2 mm MgCl2. Scale bars: 10 μm (applies to all images). C, quantification of cell surface binding in B. Data are mean ± S.E. (**, p < 0.01; ****, p < 0.0001; nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's post hoc test; number of cells analyzed = 9–19). p values for IgC binding: WT versus ΔHRD, p = 0.0841; WT versus ΔLNS, p > 0.9999; WT versus ΔStalk1, p = 0.1214; WT versus Nrxn1γ, p = 0.0616. p value for IgClstn3 binding: WT versus ΔHRD, p = 0.9581; WT versus ΔLNS, p < 0.0001; WT versus ΔStalk1, p < 0.0001; WT versus Nrxn1γ, p < 0.0001. p values for IgNL-2 binding: WT versus ΔHRD, p = 0.4988; WT versus ΔLNS, p < 0.0001; WT versus ΔStalk1, p = 0.0033; WT versus Nrxn1γ, p < 0.0001.