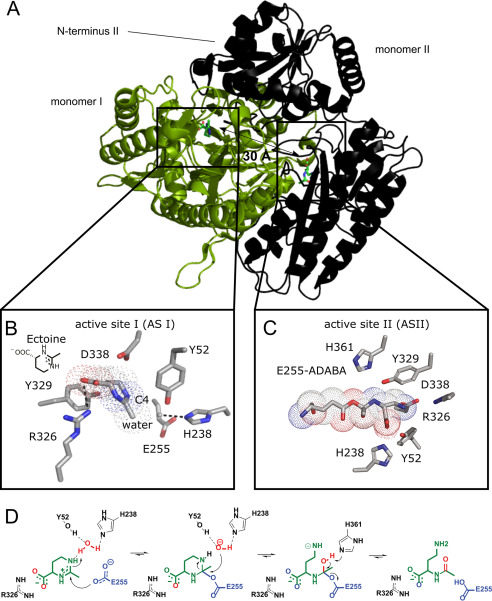
Figure 3.
Crystal structure and mechanism of EutD. A, crystal structure of the EutD homodimer with one monomer shown as green cartoon and surface and the other as black cartoon indicating secondary structure. The localization of both actives sites is depicted. B, coordination of ectoine (surrounded by a dotted outline) and the putative catalytic water in the active site of HeEutD. Ectoine is coordinated by hydrogen bonds to Arg-326. The attacking water is hydrogen-bonded by His-238. Glu-255 and Tyr-52 can be observed in proximity. C, HeEutD active site with the α-ADABA intermediate covalently bound to Glu-255 (surrounded by a dotted outline). Further hydrogen bonds by His-238, Tyr-52, and Asp-338 keep the molecule in place. D, catalytic mechanism of ectoine hydrolysis by EutD. Ectoine, the catalytic water and Glu-255 are shown in green, red, and blue, respectively.