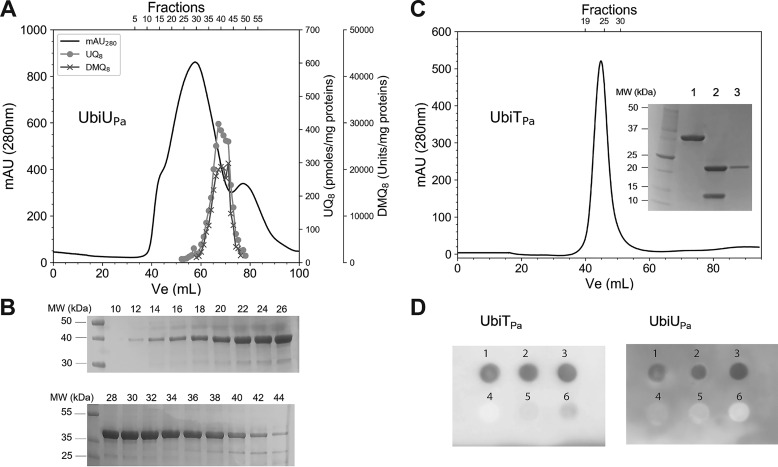
Figure 6.
Recombinant UbiUPa and UbiTPa bind UQ8. A, Elution profile of UbiUPa. 70 mg of protein was loaded on a Superdex 200 16/60 chromatography column. Quantification of UQ8 and DMQ8 in each fraction was performed by HPLC-ECD MS. Recovery of 73 and 76%, respectively, for UQ8 and DMQ8 was calculated from the total content of all fractions compared with content of the UbiUPa-purified fraction deposited in the Superdex 200 column. B, Fractions 10–44, analyzed by SDS-PAGE for purity. C, Elution profile of UbiTPa on a Superdex 200 16/60 column. Inset, SDS-PAGE. Lane 1, 32-kDa TrxA-UbiTPa fusion protein; lane 2, after digestion with thrombin (UbiTPa, 19.6 kDa; TrxA, 12.1 kDa); lane 3, pooled fractions 20–30 of UbiTPa. Quantification of UQ8 (pool of fractions 20–30) was performed by HPLC-ECD MS. D, Protein-lipid overlay assay between UbiUPa and UbiTPa and different lipid ligands. 2 μl of six different lipid/compound potential candidates (1, UQ8; 2, UQ10; 3, solanesol; 4, 3-methylcatechol; 5, cholesterol; 6, POPE) at 20 mm final concentration were spotted on a PVDF membrane and then incubated with UbiTPa or UbiUPa (both proteins at 0.2 µg/ml final concentration). Detection of bound proteins was performed by chemiluminescence, as described in Experimental procedures. MW, molecular weights.