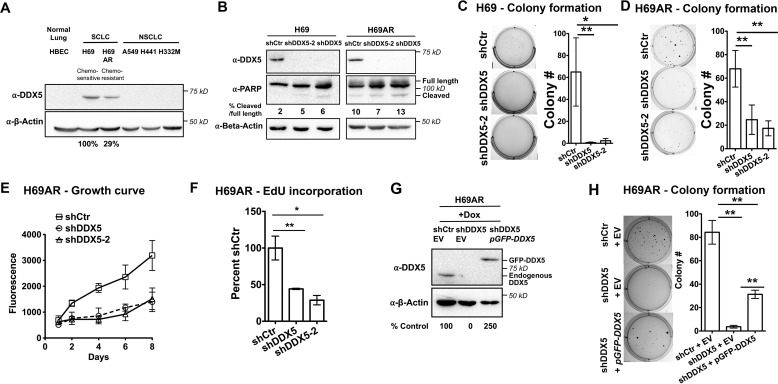
Figure 1.
Knockdown of DDX5 reduces proliferation and soft agar colony formation of SCLC cells. A, Western blotting of DDX5 in HBEC, SCLC, and NSCLC cell lines. B, Western blotting of DDX5 and PARP in H69 and H69AR cells stably transfected with shRNAs targeting DDX5 or with a nontargeting control (shCtr). C and D, soft agar colony formation assays of H69 or H69AR cells, with or without DDX5 knockdown. 10,000 cells/well of H69 cells or 5000 cells/well of H69AR cells were seeded in a 0.3% agar layer in 6-well plates. H69 and H69AR cells were grown for 30 and 21 days, respectively, with growth medium added twice a week. The bar graphs in the right panels show colony counts from at least three replicates, whereas the left panels show representative pictures of wells. E, growth curve of H69AR cells with or without DDX5 knockdown. H69AR cells were seeded at 200 cells/well in 96-well plates on day 0, and the relative cell number was measured on the indicated days. Cell growth was measured using CyQuant fluorescent DNA dye to quantify cell number on the days indicated. The data show the means ± S.D. of four biological replicates. F, measurement of cell proliferation by quantifying newly synthesized DNA using the nucleotide analog EdU after 24 h of growth. Incorporated EdU was measured using the Click-iT EdU Alexa Fluor 647 Assay (Invitrogen, C10356). G, Western blotting of DDX5 in H69AR cells expressing shRNA-resistant GFP–DDX5. GFP–DDX5 is overexpressed as compared with endogenous DDX5. H, soft agar assays of cells expressing GFP–DDX5. Ectopic overexpression of GFP–DDX5 partially rescues the ability of H69AR cells to form colonies in soft agar. The bar graph shows colony counts from three biological replicates, and the left panel shows one representative picture for each cell line. Colonies were quantified using OpenCFU. The data show the means ± S.D. of three biological replicates. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. EV, empty vector; Dox, doxycycline.