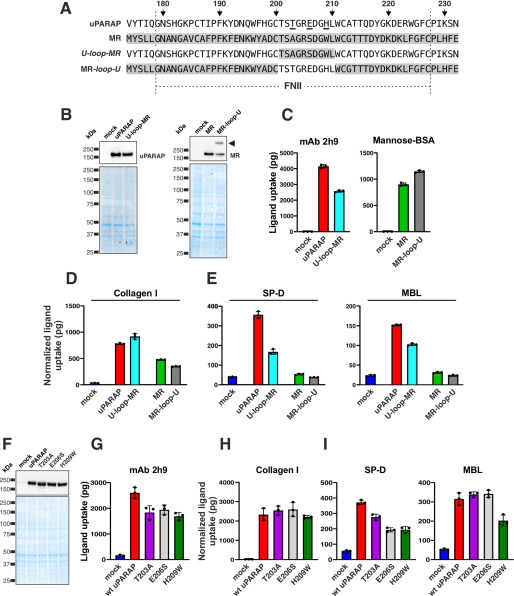
Figure 4.
Amino acid residues Thr-203, Glu-206, and His-209 are critical for the interaction of uPARAP with collectins. A, alignment of FNII domain sequences from uPARAP, MR, U-Loop-MR, and MR-Loop-U (u-Loop-MR, uPARAP mutant receptor with residues Thr-201–Leu-210 replaced by the corresponding residues from MR (Thr-183–Leu-192); MR-Loop-U, MR mutant receptor with residues Thr-183–Leu-192 replaced by the corresponding residues from uPARAP (Thr-201–Leu-210)). The amino acid numbering indicated at the top of the panel follows the uPARAP sequence. B, western blotting analysis for the detection of uPARAP (top left) or MR (top right) in CHO-K1 cells transfected with the indicated constructs (top panel). Loading controls were included as described in the legend to Fig. 1 (bottom panel). Note, the presence of an extra band in the MR-loop-U mutant lane (arrowhead; possibly representing an MR dimer) was considered of minor functional importance, judged from the uptake of mannose-BSA and collagen mediated by this mutant receptor (C and D). C–E, assay for uptake of radiolabeled mAb 2h9 and mannose-BSA (C), collagen type I (D), and SP-D and MBL (E) by mock CHO-K1 cells and cells expressing uPARAP, MR, or the indicated mutants. F, western blotting analysis for the detection of uPARAP in HEK-293T cells transfected with the indicated constructs (top panel). Loading controls were included as described in the legend to Fig. 1 (bottom panel). G–I, assay for uptake of radiolabeled mAb 2h9 (G), collagen type I (H), and SP-D and MBL (I) by mock HEK-293T cells and cells expressing WT uPARAP or indicated mutants. The uptake of collagen type I, SP-D, and MBL was normalized to the uptake of anti-uPARAP antibody 2h9 (uPARAP, U-loop-MR, T203A, E206S, and H209W) or mannose-BSA (MR and MR-loop-U) to adjust for differences in the receptors' expression levels (see “Experimental procedures”). Data are presented as mean ± S.D. with individual data points also shown. Analysis was performed in triplicate (C–E and G–I).