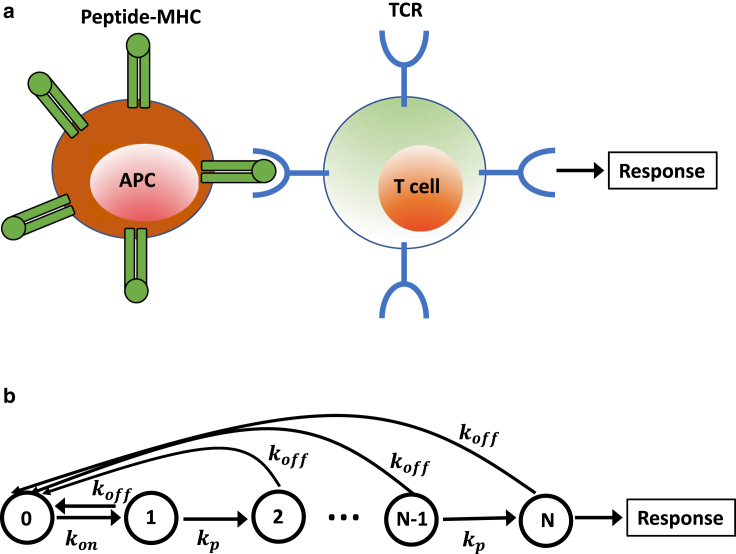
Figure 1.
(a) A schematic description of the activation of a T cell during the immune response. A T cell binds via a TCR to an antigen-presenting cell. If a foreign peptide is identified, the response is activated. (b) shows a schematic view of the simplest kinetic proofreading model for the antigen discrimination. Each state n (1 ≤ n ≤ N) corresponds to a complex between TCR and pMHC with different degrees of phosphorylation. State n = 0 describes the unbound TCR and pMHC species. The immune response is activated when the system reaches the state n = N and the stationary concentration of this state is achieved. To see this figure in color, go online.