Figure 5.
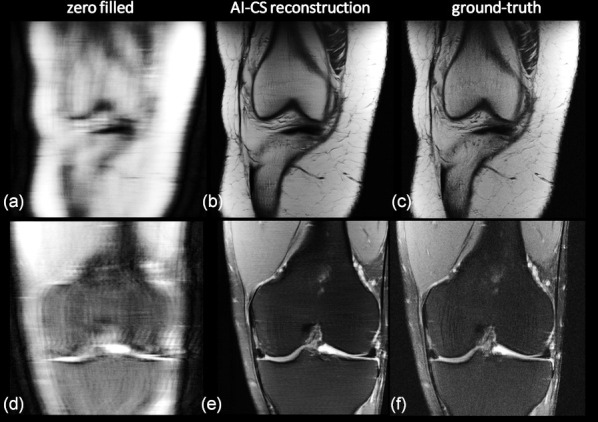
Accelerating MRI using an iterative AI/deep learning-based compressed-sensing approach. Clinical knee data (arXiv 1811.08839, 2018) measured with a 15-channel knee coil at two different contrasts were retrospectively variable density under-sampled and reconstructed. (a,d) Using zero filling, Fourier transform and coil image combination, (b,e) by an iterative AI-CS approach, whereas (c,f) show the ground truth for comparison. (top row: proton density, acceleration factor: 7.9, bottom row: T2 weighted data, acceleration factor: 9.7). A quite high correspondence between the AI-driven reconstruction and the ground truth can be found and the ability to gently de-noise can be appreciated too. The reconstructions shown in the middle are from the winner of the fMRI reconstruction challenge multi-coil 8x and co-winner of the multi-coil 4x; courtesy Nicola Pezzotti, et al. ‘Philips & LUMC’ team (arXiv 1912.12259, 2019).
