Figure 5.
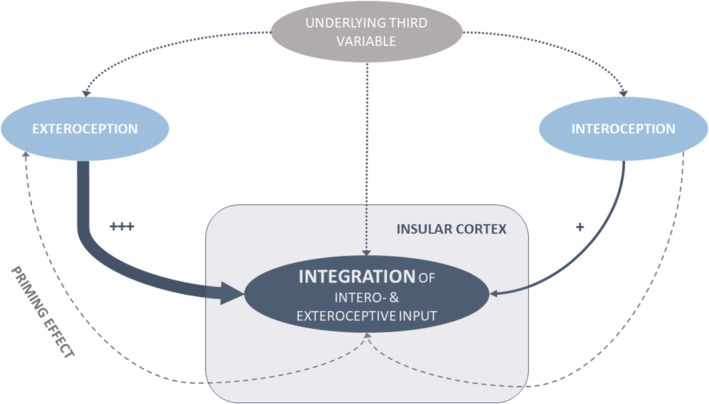
Overview of explanatory models describing the coherence of intero‐ and exteroception. Main explanatory model: External stimuli such as olfactory stimulation trigger (+++) the integration of both, extero‐ and interoceptive input, reflected in enhanced neuronal responses in the central dorsal insular cortex. Alternative model 1: Interoceptive sensations serve as priming factors for incoming external sensations. Alternative model 2: A common underlying variable such as situational attention influences both intero‐ and exteroception
