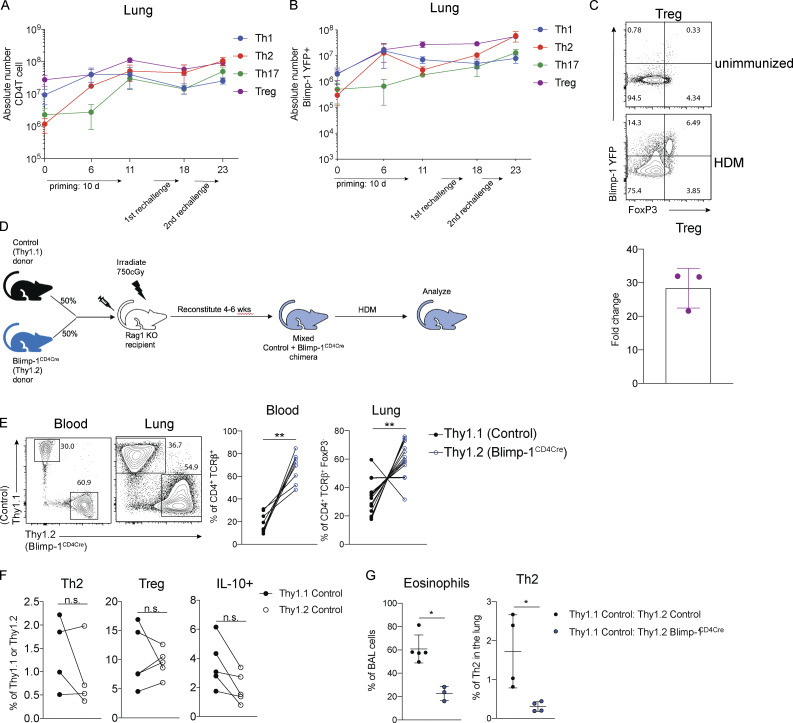
Figure S3.
Blimp-1 expression dynamics in HDM-induced allergic lung inflammation. (A) Absolute number of CD4 T cell subsets during the course of HDM-induced allergic lung inflammation model. (B) Absolute number of Blimp-1 YFP+ cells of each CD4 T cell subset shown in A. (C) Flow analysis and fold change of Blimp-1 YFP+ FoxP3+ T reg cells in the lung of naive unimmunized animals and after HDM. Fold change calculated as percent of Blimp-1 YFP+ T regs after HDM over average of Blimp-1 YFP+ T reg cells in unimmunized mice. Data in A–C are from two experiments with three mice per group. (D) Schematic of mixed BM chimera generation. (E) Reconstitution 4–6 wk after irradiation and injection of donor marrow isolated from blood (4 wk) or lungs after HDM-induced lung inflammation. Flow cytometry and percent of Thy1.1+ (control) and Thy1.2+ (Blimp-1CD4Cre) in both tissues shown. Data in E are pooled from two experiments with 14 mixed BM chimeras, mean ± SD. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. (F) Percent of Th2, T reg, and IL-10+ cells in 50:50 mixed Thy1.1 control: Thy1.2 control BM chimeras in the lung after HDM immunization. Th2 and IL-10+ cells gated on CD4+ TCRb+ FoxP3- Thy1.1+ or Thy1.2+. T reg cells gated on CD4+ TCRb+ FoxP3+ Thy1.1+ or Thy1.2+. (G) Percent of eosinophils and total Th2 cells in the lungs of 50:50 mixed Thy1.1 control: Thy1.2 control or 50:50 mixed Thy1.1 control: Thy1.2 Blimp-1CD4Cre BM chimeras. Data in F and G are pooled from two experiments with five mixed BM chimeras, mean ± SD. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. **, P < 0.01.