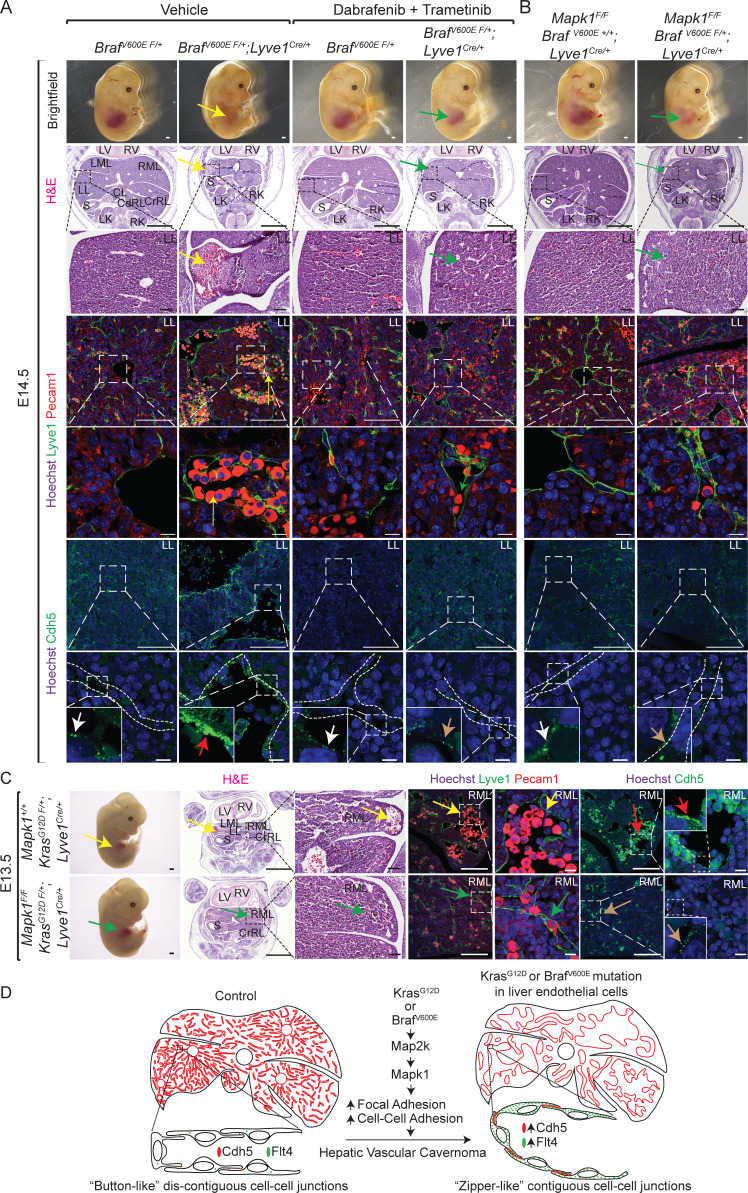
Figure 4.
Pharmacologic inhibition of BrafV600E-Map2k or genetic ablation of Mapk1 rescue hepatic vascular cavernomas in BrafV600E F/+; Lyve1Cre and KrasG12D F/+; Lyve1Cre mice. (A and B) Dissected BrafV600E F/+; Lyve1Cre littermate embryos treated with dabrafenib and trametinib (A) or lacking Mapk1 (B) show rescued liver size (green arrows) compared with BrafV600E F/+; Lyve1Cre embryos (yellow arrow; n = 3). H&E-stained or Lyve1 (green), Pecam1 (red), and Hoechst (blue) coimmunofluorescent–stained liver sections of BrafV600E F/+; Lyve1Cre littermate embryos treated with dabrafenib and trametinib (A) or lacking Mapk1 (B) show normal sinusoidal capillaries (green arrows) compared with cavernous sinusoids in BrafV600E F/+; Lyve1Cre embryos (yellow arrows; n = 3). Immunofluorescent staining on liver sections of BrafV600E F/+; Lyve1Cre embryos treated with dabrafenib and trametinib (A) or lacking Mapk1 (B) show normal button-like discontiguous expression of Cdh5 (brown arrows) compared with abnormal zipper-like contiguous expression of Cdh5 in BrafV600E F/+; Lyve1Cre embryos (red arrows; n = 3). White arrows show normal button-like discontiguous expression of Cdh5 in control livers. Scale bars: 500 µm (top row), 1,000 µm (second row from top), 100 µm (third, fourth, and sixth rows from top), and 10 µm (fifth and seventh rows from top). Two independent experiments. (C) Dissected KrasG12D F/+; Lyve1Cre littermate embryos lacking Mapk1 show rescued liver size (green arrow), normal sinusoidal capillaries (green arrows) stained with H&E or Lyve1 (green) and Pecam1 (red), and normal button-like discontiguous expression of Cdh5 (brown arrows) compared with KrasG12D F/+; Lyve1Cre (yellow and red arrows). n = 3. Scale bars: 500 µm (first column from left), 1,000 µm (second column from left), 100 µm (third, fourth, and sixth columns from left), and 10 µm (fifth and seventh columns from left). Two independent experiments. (D) Endothelial activating KRAS or BRAF mutations drive hepatic vascular cavernomas via MAP2K–MAPK1 signaling pathway. Proposed model suggesting that constitutive activation of KRAS–BRAF–MAP2K–MAPK1 signaling pathway in sinusoidal endothelial cells promotes aberrant zipper-like contiguous expression of adherens junctional proteins, such as Cdh5, switching hepatic sinusoidal capillaries from branching to cavernous expansion. All experimental data verified in at least two independent experiments. CdRL, caudal right lobe; CL, caudate lobe; CrRL, cranial right lobe; LK, left kidney; LL, left lobe; LML, left medial lobe; LV, left ventricle; RK, right kidney; RML, right medial lobe; RV, right ventricle; S, stomach.