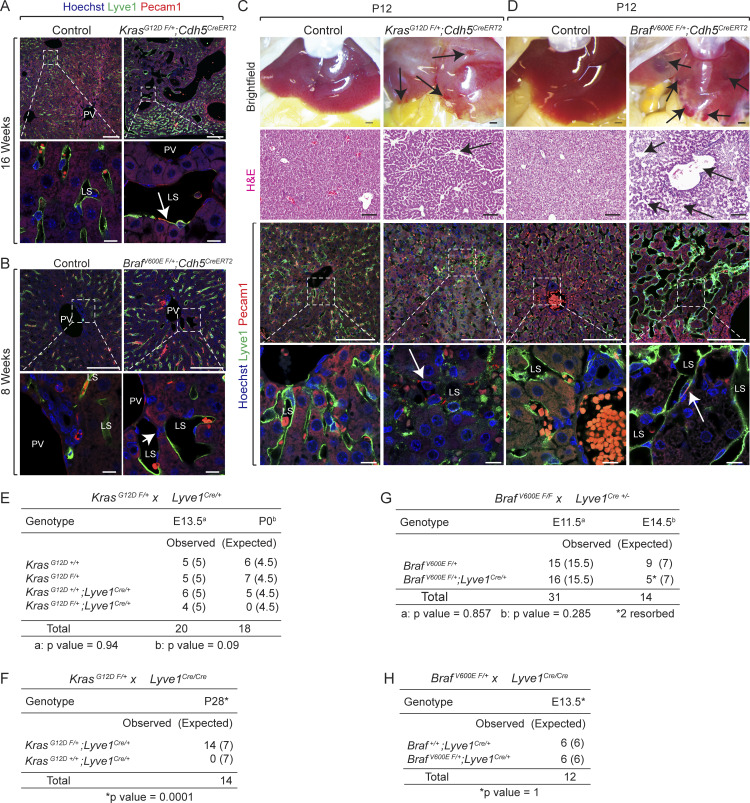
Figure S2.
Endothelial KrasG12D or BrafV600E gain-of-function mutations cause hepatic vascular cavernomas and embryonic lethality in mice. (A and B) Lyve1 (green) and Pecam1 (red) coimmunofluorescent staining with Hoechst nuclear counterstain (blue) on tamoxifen-treated adult KrasG12D F/+; Cdh5CreERT2 (A) and BrafV600E F/+; Cdh5CreERT2 (B) liver sections shows contribution of Lyve1+ and Pecam1+ endothelial cells to hepatic vascular cavernomas (white arrows). n = 3. Scale bars: 100 μm (top row) and 10 µm (bottom row). Two independent experiments. (C and D) Dissected livers and H&E-stained liver frontal sections show vascular cavernomas (black arrows) in tamoxifen-treated KrasG12D F/+; Cdh5CreERT2 (C) and BrafV600E F/+; Cdh5CreERT2 (D) neonatal mice. Lyve1 (green) and Pecam1 (red) coimmunofluorescent staining with Hoechst nuclear counterstain (blue) on KrasG12D F/+; Cdh5CreERT2 (C) and BrafV600E F/+; Cdh5CreERT2 (D) liver sections shows contribution of Lyve1+ and Pecam1+ endothelial cells to hepatic vascular cavernomas (white arrows). n = 3. P, postnatal day. Scale bars: 500 μm (top row), 100 µm (second and third rows from top), and 10 µm (bottom row). Two independent experiments. (E and F) Genotyping tables of embryos or pups derived from KrasG12D F/+ mice crossed with either Lyve1Cre/+ (E) or Lyve1Cre/Cre (F) mice. (G and H) Genotyping tables of embryos derived from BrafV600E F/F (G) or BrafV600E F/+ (H) mice crossed with either Lyve1Cre/+ (G) or Lyve1Cre/Cre (H) mice. χ2 P value 0.94 (E, E13.5), 0.09 (E, P0), 0.0001 (F), 0.857 (G, E11.5), 0.285 (G, E14.5), 1.0 (H). LS, liver sinusoid; PV, portal vein.