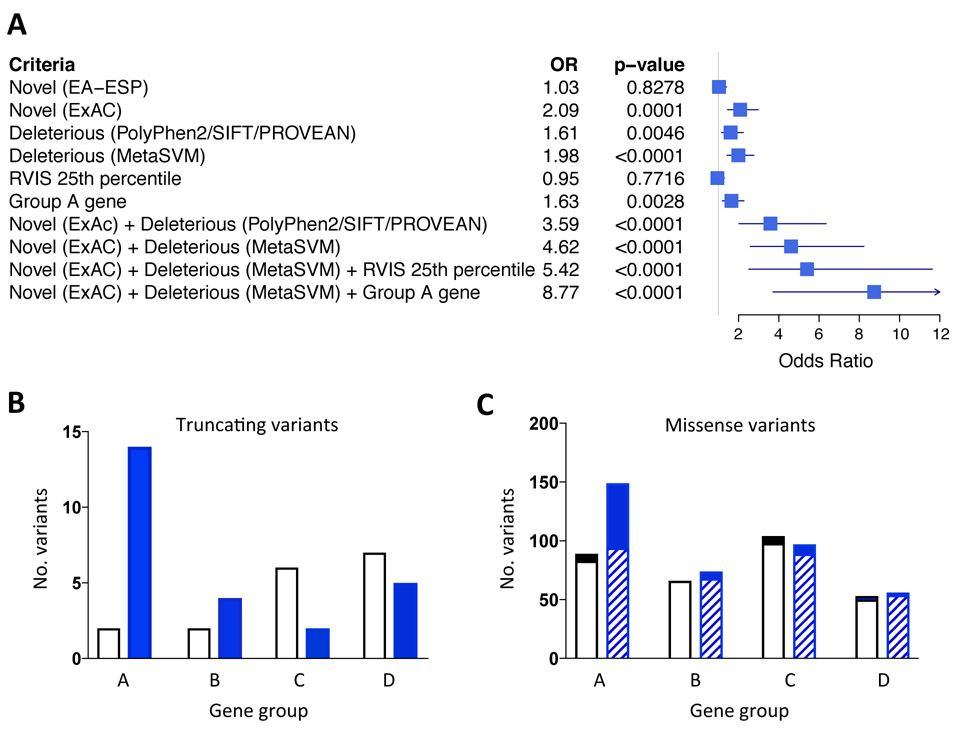
Figure 1.
Criteria for variant prioritization. (A) Missense rare variants in cardiomyopathy genes in DCM cases and controls were compared using a number of criteria including novelty, defined as absence from the European subgroup of the Exome Sequencing Project (EA-ESP) or Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC), in silico functional predictions (PolyPhen2, SIFT, PROVEAN, MetaSVM), RVIS score and gene group. The odds ratios (OR) for DCM are displayed in a forest plot. (B) Distribution of truncating variants across gene groups in controls (white bars) and DCM cases (blue bars). (C) Distribution of missense variants across gene groups in controls (white bars) and DCM cases (blue bars). The subset of “novel (ExAC) + deleterious (MetaSVM)” missense variants are denoted in the solid sections of bars. There were significant effects of clinical status and gene group for truncating variants (B, P = 0.01; 2 x 4 chi-squared test) and missense variants (C; P = 0.018); see Supplementary Table S6 for statistical analysis. For all panels, TTN truncating and missense variants were excluded.