Extended Data Fig. 5. Effects of TRIP13 deficiency in TLS assays.
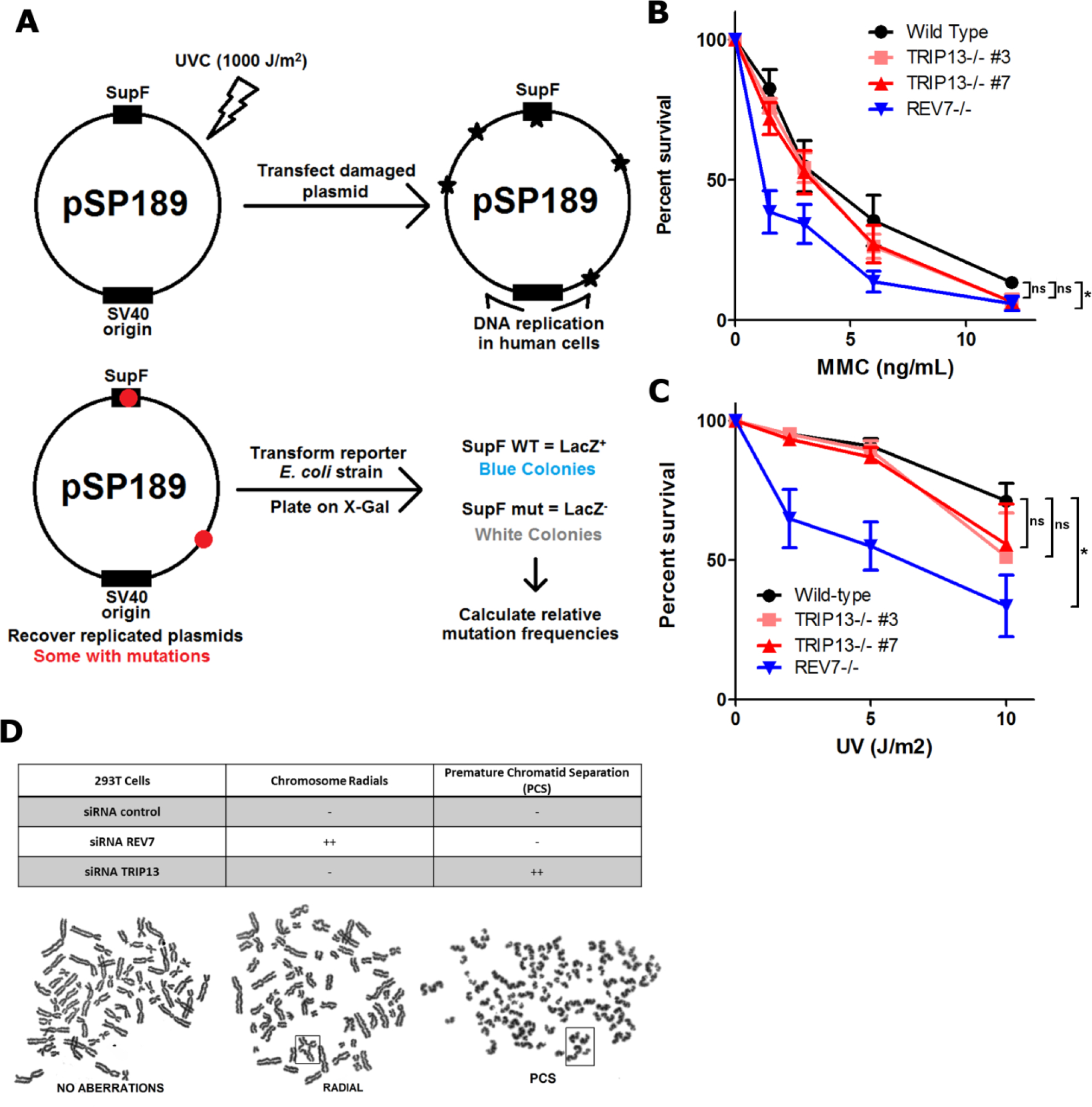
a. Schematic of the SupF assay. Plasmids are damaged by exposure to a high UV dose. Damaged plasmids are transfected into HEK293T cells and allowed to replicate, accumulating mutations. Plasmids are isolated from cells and transformed into a reporter E. coli strain. Functional SupF expression allows for readthrough of a premature stop codon in the LacZ gene. Any mutations in SupF give LacZ- colonies. b. 14-day clonogenic survival assay of U2OS wild-type, TRIP13−/− or REV7−/− cell lines treated with indicated mitomycin C (MMC) doses. n=3 biologically independent experiments, Wild-type vs. TRIP13−/− #3: p = 0.19, Wild-type vs. TRIP13−/− #7: p = 0.15, Wild-type vs. REV7−/−: p < 0.0001 (2-Way ANOVA) c. 14-day clonogenic survival assay of U2OS wild-type, TRIP13−/− or REV7−/− cell lines treated with indicated UV doses. n=4 biologically independent experiments, Wild-type vs. TRIP13−/− #3: p = 0.23, Wild-type vs. TRIP13−/− #7: p = 0.21, Wild-type vs. REV7−/−: p < 0.0001 (2-Way ANOVA). d. (Top) Table summarizing effect of nontargeting, REV7- or TRIP13-targeting siRNAs on chromosome radial formation, a hallmark of FA pathway dysfunction, and premature chromatid separation (PCS), indicative of SAC dysfunction. (Bottom) Metaphase spreads from HEK293T cells transfected with specified siRNAs showing radials and PCS in boxes.
