Figure 3.
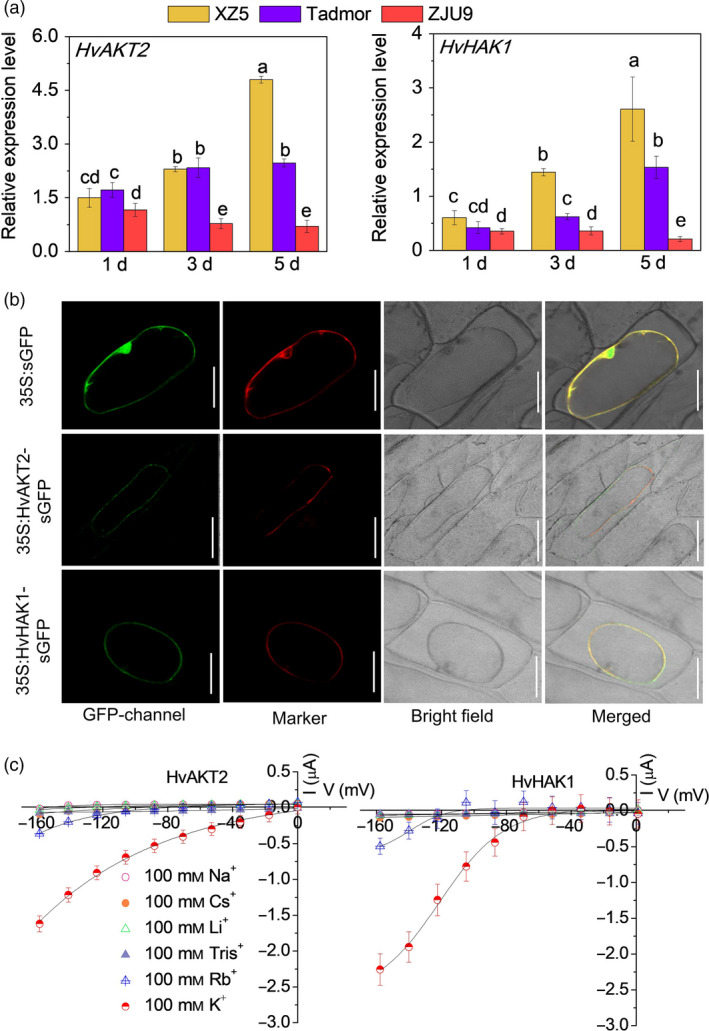
Subcellular localization and electrophysiology of HvAKT2 and HvHAK1. (a) Real‐time PCR analysis of HvAKT2 and HvHAK1 in three barley genotypes XZ5, Tadmor and ZJU9 subjected to PEG treatment. (b) Subcellular localization of the GFP, HvAKT2‐ and HvHAK1‐sGFP fusion proteins in onion epidermis cells. A plasma membrane RFP marker protein (pm‐rb CD3‐1008) was used as a reference. Bars = 50 μm. (c) Ion transport characteristics of HvAKT2 and HvHAK1 in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Holding potential was −20 mV, and voltage was clamped from −160 to 0 mV for 10 cycles. Data are mean ± SE (10–15 oocytes from at least three independent experiments).
