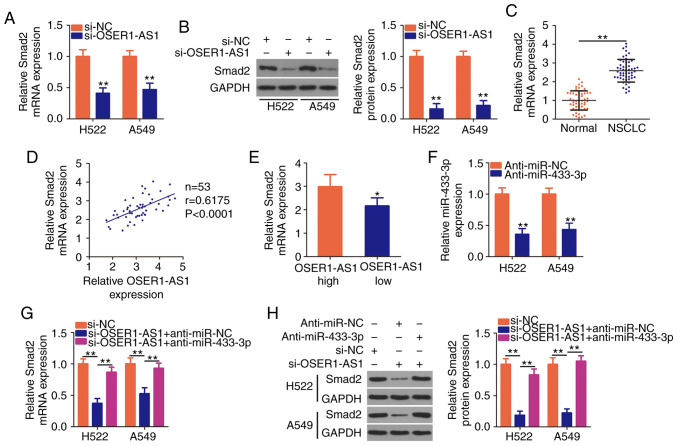
Figure 4.
OSER1-AS1 knockdown suppresses Smad2 expression in NSCLC cells. (A and B) Detection of Smad2 mRNA and protein expression in OSER1-AS1-deficient H522 and A549 cell lines by RT-qPCR and western blotting, respectively. **P<0.01, compared with the si-NC group. (C) Determination of Smad2 mRNA expression in 53 pairs of NSCLC tissues and adjacent normal tissues using RT-qPCR. **P<0.01. (D) Spearman's correlation analysis of the correlation between OSER1-AS1 and Smad2 mRNA expression in the 53 NSCLC tissues (r=0.6175, P<0.0001). (E) Comparison of Smad2 expression in NSCLC tissues derived from patients in the high- and low-OSER1-AS1 expression groups. *P<0.05, compared with the OSER1-AS1 high group. (F) miR-433-3p expression in H522 and A549 cells transfected with anti-miR-433-3p or anti-miR-NC using RT-qPCR. **P<0.01, compared with the anti-miR-NC group. (G and H) Cotransfection of OSER1-AS1-deficient H522 and A549 cells with anti-miR-433-3p or anti-miR-NC and detection of Smad2 protein expression using RT-qPCR and western blotting, respectively. **P<0.01. OSER1-AS1, RNA OSER1 antisense RNA 1; Smad2, mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2; miR, microRNA; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction.