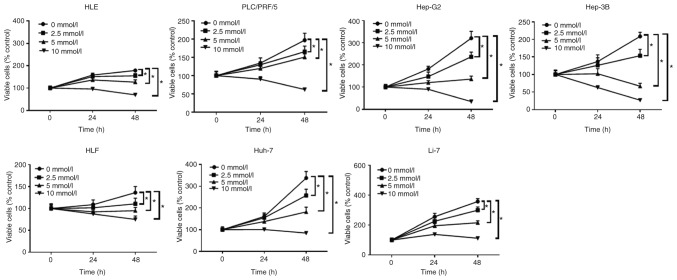
Figure 1.
Aspirin inhibits the proliferation of human HCC cells and a hepatoblastoma cell line. All cell lines were treated with 0, 2.5, 5, or 10 mmol/l aspirin for 24 or 48 h. The data points represent the mean cell number from three independent cultures, and the error bars represent standard deviations (SDs). The antiproliferative effect of the aspirin treatment was significantly higher in the HCC and liver cancer cells at 48 h when compared to the untreated control cells (0 mmol/l) by two-way ANOVA (*P<0.01, vs. the control). HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma.