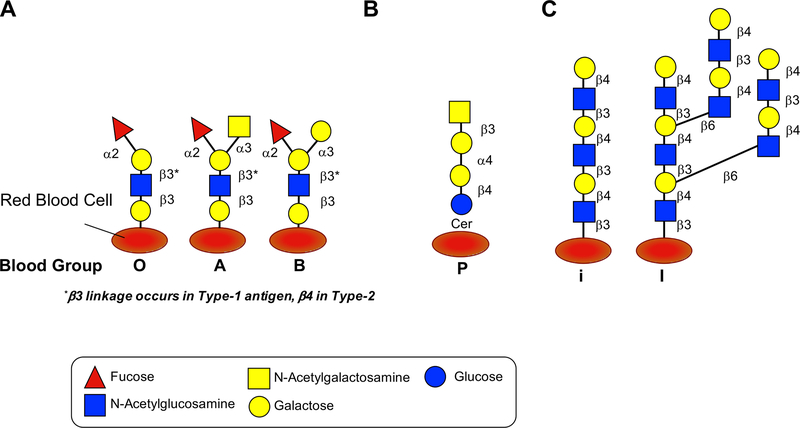
Figure 2. Common blood group glycan structures.
A. Blood group antigens are surface markers on the outside of the red blood cell membrane. Blood group antigens are proteins (not shown) and carbohydrates attached to lipid or protein. A model for the major carbohydrate types of blood group antigens is shown. Variations in linkage can lead to variations, shown is Type 1 vs. Type 2 where b-linkage is a determinant. Further Type 3 and Type 4 variations exist (not shown). B. A common P blood group, in which the antibodies against this antigen is produced in individuals with paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria (PCH), is also shown. C. The blood group precursor structure termed “i” which is present in newborns and is extended by age two by adding 1) β6 galactose to form “I”; 2) blood group O by adding α2 fucose; blood group A by adding α2 fucose and α3 N-acetylglucosamine; blood group B by adding α2 fucose and α3 galactose.