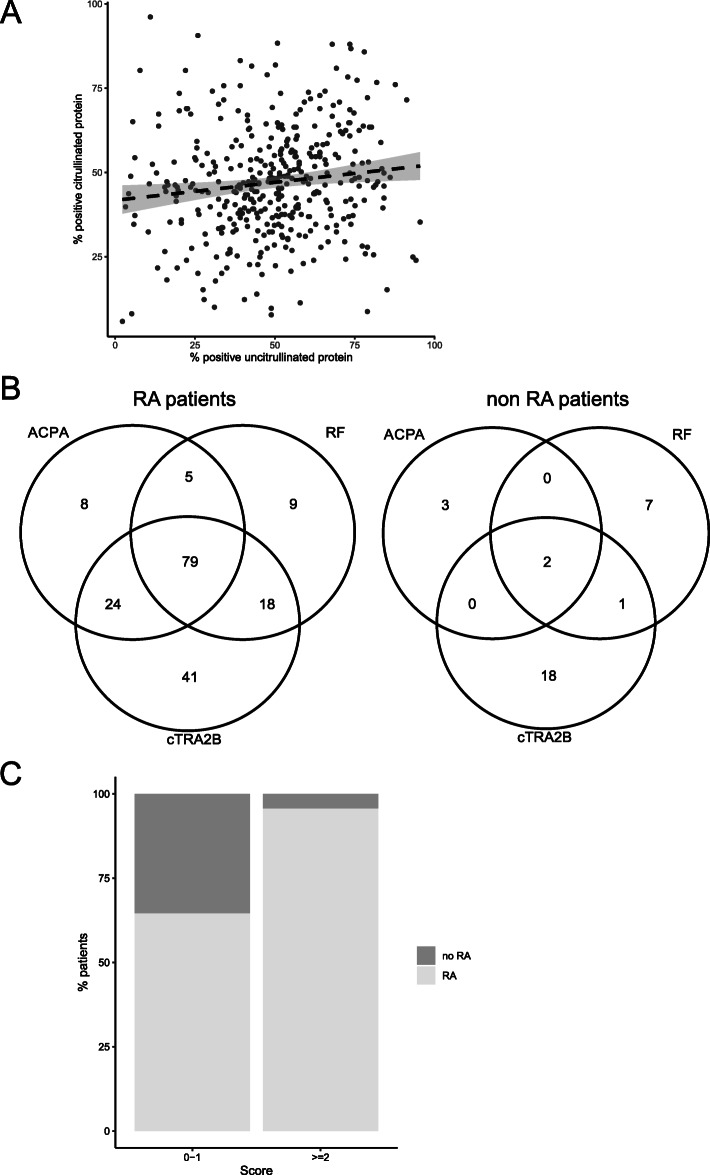
Fig. 1.
a Detection rates of IgG antibodies to citrullinated and uncitrullinated forms of 390 distinct proteins in patients diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis (RA patients) (n = 309) out of an early arthritis cohort (n = 411). Each dot represents the percentage of patients with an increased IgG detection towards a distinct citrullinated or uncitrullinated protein. Regression line with 95% confidence interval depicted (Spearman’s r = 0.13, p = 0.01). b Venn diagram representing the number of patients with increased antibody reactivity in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients and control patients (non-RA patients) classified as RA by three distinct autoantibodies against citrullinated peptides (ACPA), citrullinated “transformer 2 beta homolog” (cTRA2B), and rheumatoid factor (RF) as well as the respective overlaps. c Proportion of patients who were subsequently diagnosed with RA or not according to a diagnostic score of ≥ 2 (n = 140) or below (n = 271) based on adjusted odds ratios of multivariable generalized linear modeling (ACPA 3 points, RF and cTRA2B 1 point each)