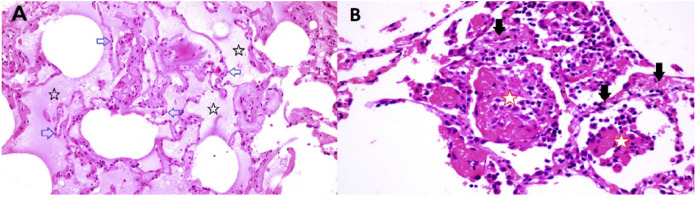
Figure 9.
Lung pathology of early COVID-19 84 year old female undergoing right middle lobe (RML) resection for adenocarcinoma. On Day 6 of hospitalization a CT scan showed a ground glass opacity (GGO) in the RML in addition to the tumor mass. Lobectomy was performed on Day 12. On Day 13 (Day 1 post-operation), CT scan showed bilateral bibasilar GGO. On Day 16, she developed typical COVID-19 symptoms with cough, dyspnea and chest tightness. Capillary O2 saturation ranged from 77–88%. Death ensued on Day 29. SARS-CoV-2 was confirmed by nasal swab. (Tian et al 59) Panel A (RML). There is extensive pulmonary edema consistent with a transudate (open black stars). Alveolar septae appear normal and there is no inflammation (open blue arrows). Features are not suggestive of an infection. Panel B (RML) There is fibrinous exudate in the alveolar spaces (open red stars). Alveolar septae show edema and a mononuclear infiltrate (solid black arrows). No neutrophils are identified. There is no significant diffuse alveolar damage of ARDS. Features are typical of an interstitial viral pneumonia.