Figure 1.
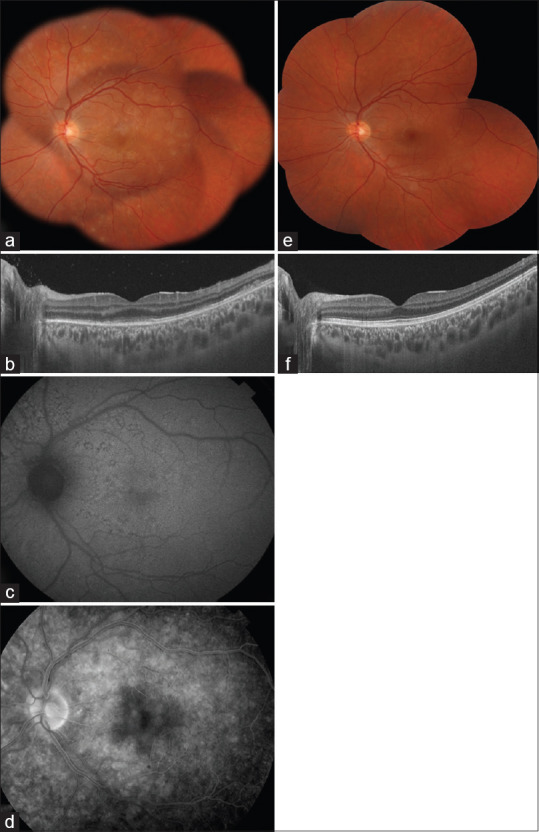
Multimodal imaging of a 25-year-old patient during the acute phase of multiple evanescent white dots syndrome. (a) Composite color fundus photograph of the left eye showing multifocal, deep, white lesions in the posterior pole and mid-periphery associated with foveal granularity. (b) Structural swept-source optical coherence tomography (SS-OCT) demonstrating disruption of the ellipsoid zone and accumulations of a hyperreflective material over the retinal pigment epithelium. (c) Near-infrared fundus autofluorescence showing multiple hypoautofluorescent spots. (d) Fluorescein angiography showing late diffuse multifocal hyperfluorescence with a “wreath-like” configuration around the fovea and optic disc leakage. (e) Composite color fundus photograph of the left eye, 6 months after the initial presentation, showing the resolution of the white retinal lesions. (f) Structural SS-OCT, 6 months after the first presentation, showing normal outer retinal layers
