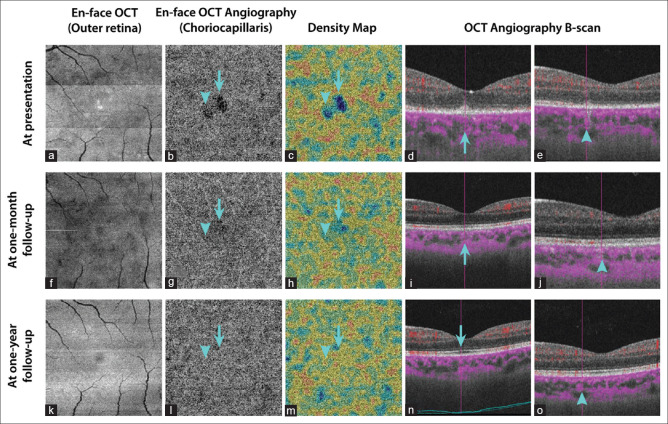
Figure 4.
En-face swept-source optical coherence tomography (SS-OCT) and SS-OCT angiography (SS-OCTA) at presentation in the same patient of Figure 3 (a-e): Structural en-face SS-OCT (3 mm × 3 mm scans) at the level of the outer retina revealing hyporeflective areas corresponding to the ellipsoid zone disruption and a few hyperreflective spots due to the accumulations of hyperreflective material over the retinal pigment epithelium. En-face SS-OCTA (3 mm × 3 mm scans) at the level of choriocapillaris showing areas of hypointense flow deficit, which are highlighted by an arrow and an arrowhead, respectively, with decreased flow signal in the choriocapillaris on respective SS-OCTA B-scans. Both the areas of flow voids that are shown are associated with inflammatory changes of the overlying outer retina, and a projection artifact with a signal attenuation could not be excluded. En-face SS-OCT and SS-OCTA, at 1-month follow-up (f-j): En-face SS-OCTA, 1 month after the first presentation, showing a resolution of the hypointense areas at the level of the choriocapillaris with a restitution of flow signals on SS-OCTA B-scans. En-face SS-OCT, 1 month after the first presentation, showing some persistent hyporeflective areas. En-face SS-OCT and SS-OCTA, at 12-month follow-up (k-o): En-face SS-OCT at the level of the outer retina and SS-OCTA at the level of the choriocapillaris, 1 year after the first presentation, showing no obvious abnormalities