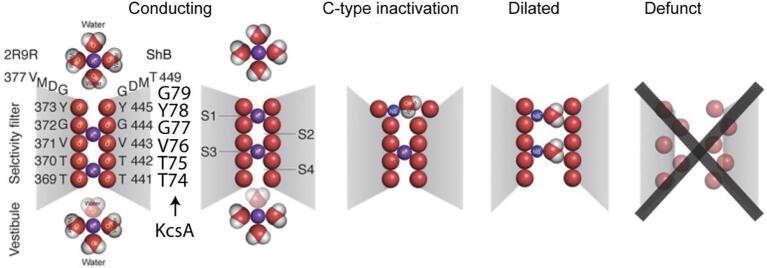
Fig. 9.
The ion dilation hypothesis proposed by Armstrong et al. to explain the inactivation process in Shaker channel. The C-type inactivation starts with a local deformation at the outer mouth of the selectivity filter, which blocks the ion flow. After the potassium ions are depleted from the selectivity filter, the channel dilates and allows partially dehydrated sodium ions to flow through the channel. The channel eventually enters a defunct state, in which the selectivity filter is in a collapsed conformation. Adapted from reference (Hoshi and Armstrong, 2013).