Figure 2c.
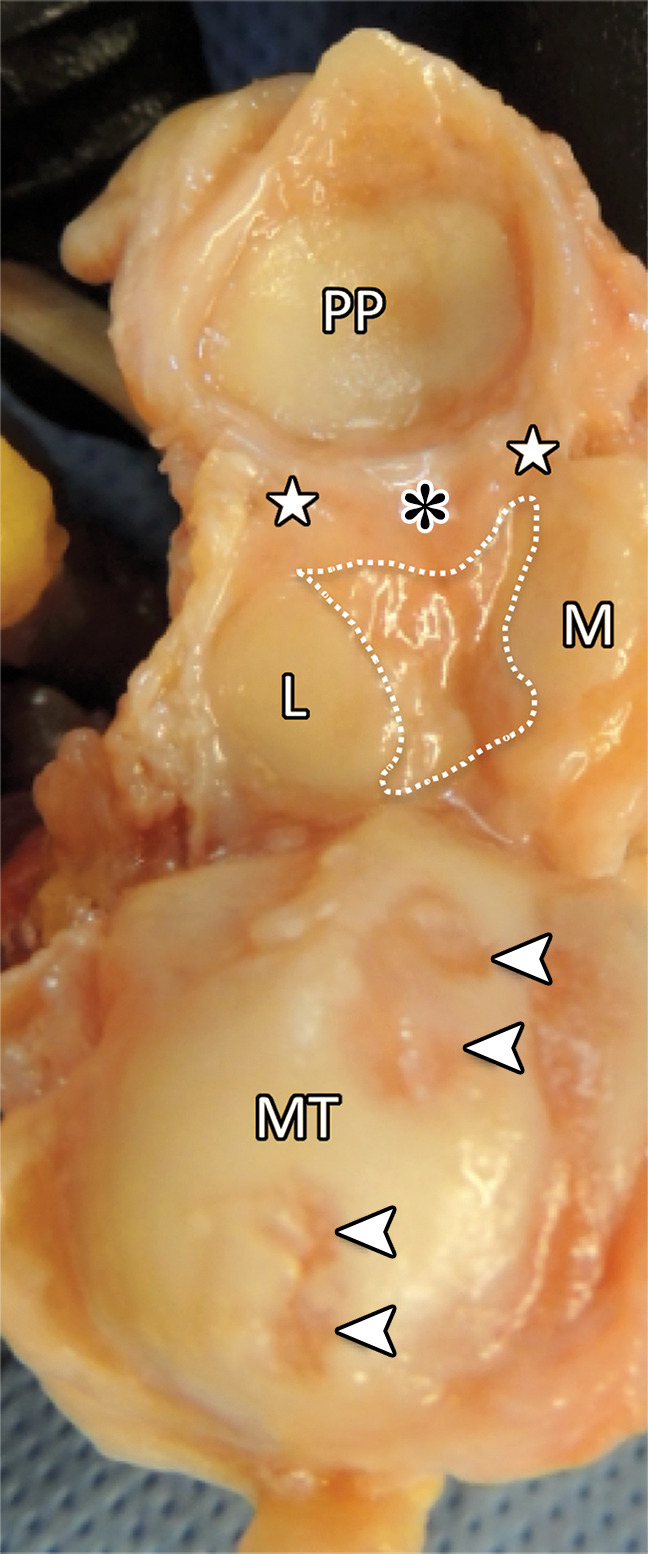
First MTPJ anatomy. (a) Drawing depicts a view from below the first MTPJ musculotendinous structures. Laterally, the oblique (ADo) and transverse (ADt) heads of the adductor hallucis provide resistance to medial displacement. Medially, the abductor hallucis tendon (AB) inserts at the medial sesamoid (M) and medial capsuloligamentous structures, preventing hallux valgus. The lateral (FHBl) and medial (FHBm) heads of the FHB insert at the respective sesamoids, preventing distal sesamoid migration. Inset in a shows the MTPJ with the FHL and tendons removed. IS = intersesamoid ligament. (b, c) Gross anatomy of a cadaveric first MTPJ specimen (b) is also shown with the medial structures dissected and then with plantar disarticulation, with the plantar plate complex (c) viewed from the dorsal aspect. Paired SPLs (☆) and the medial SPL (arrow in b) are continuous with the capsule and fibrocartilaginous pad (*), preventing proximal sesamoid migration. The ISL (dotted line in c) prevents sesamoid splaying. Chondral defects are noted at the metatarsal head (arrowheads in c). L = lateral sesamoid, MT = metatarsal, PP = proximal phalanx.
