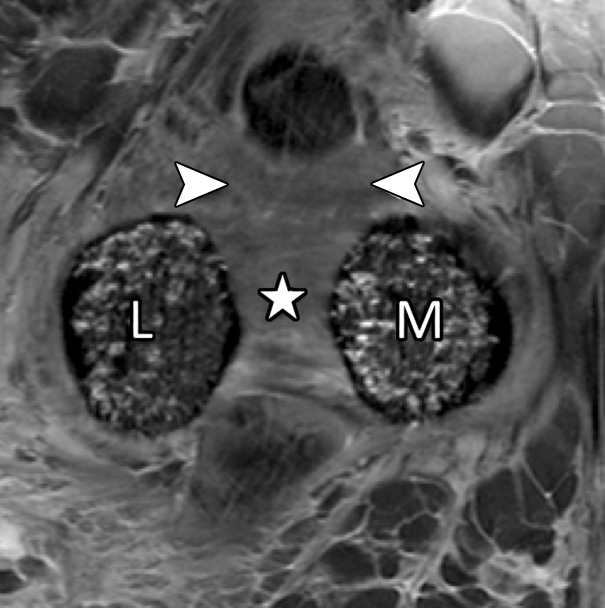
Figure 3a.
First MTPJ anatomy in a cadaveric specimen. Axial (a), central sagittal (b), and medial sagittal (c) gradient-echo images (5000/10) show how the lateral (L) and medial (M) sesamoids are connected by the ISL (☆). A fibrocartilaginous pad (arrowheads) is seen distal to the ISL, which merges with the medial SPL (black arrow) and lateral SPL (not shown). Dorsally, the EHB tendon (dotted arrow) attaches to the proximal phalanx and lies deep to the EHL tendon (white arrow).