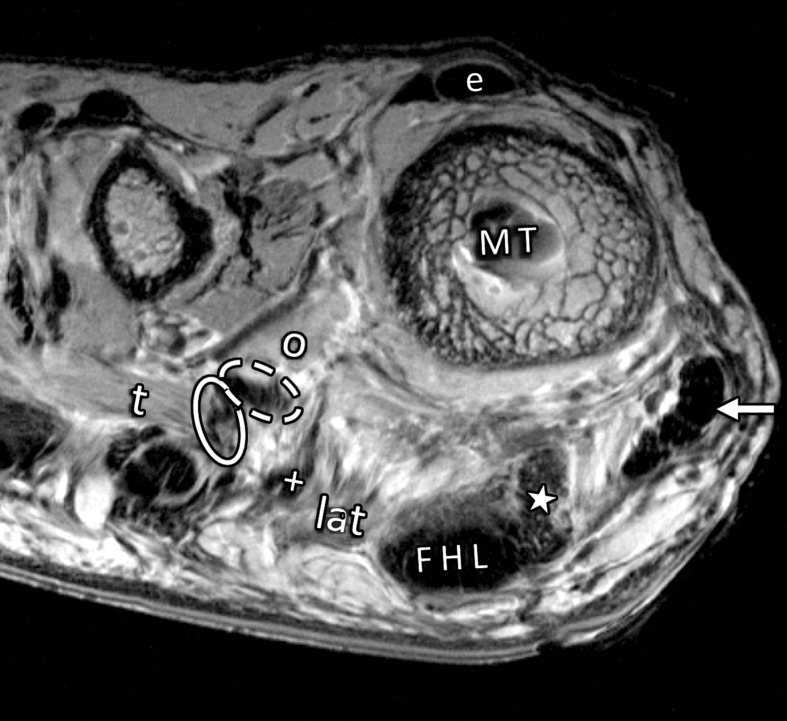
Figure 6b.
Musculotendinous structures of the first MTPJ. Coronal PDW images (2000/35) of the metatarsosesamoid joint (a) and the distal first metatarsal (MT) (b) depict the attachment of the adductor (dotted arrow) and abductor (solid arrow) hallucis tendons to the lateral (L) and medial (M) sesamoids. These tendons insert in close relation to the lateral (#) and medial (*) MTSLs and the lateral (+ = tendon, lat = muscle belly) and medial (☆) heads of the FHB. The adductor hallucis conjoint tendon is formed from the transverse (t = muscle, solid oval = tendon) and oblique (o = muscle, dashed oval = tendon) heads. Dorsally, the extensor tendons (e) can be seen secured by the lateral and medial sagittal bands (arrowheads).