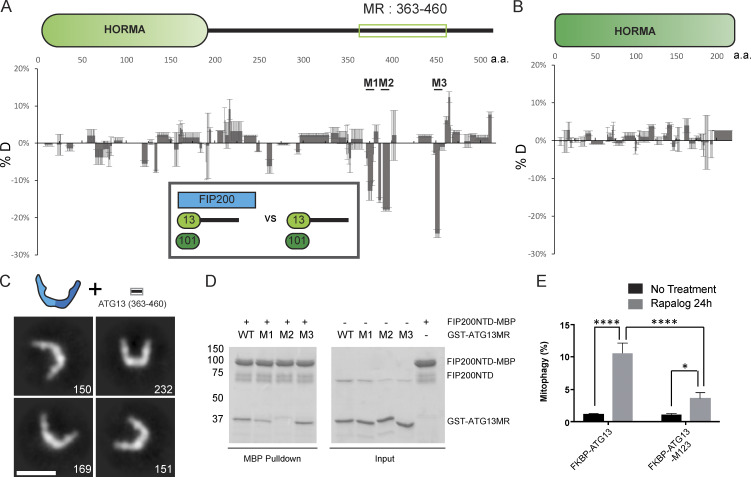
Figure 3.
Mapping the FIP200NTD binding sites on ATG13. (A) Difference of HDX percentages of the ATG13 in ATG13:ATG101 versus ATG13:ATG101:FIP200 at 6-s time point. Sites of mutation are labeled above matching residues. The MR region is highlighted with the unfilled rectangular green box, as labeled. All values are mean ± SD. (B) Difference of HDX percentages of the ATG101 in ATG13:ATG101 versus ATG13:ATG101:FIP200. All values are mean ± SD. (C) NSEM 2D class averages of FIP200NTD:ATG13 MR complex. The two color shades in the cartoon C-shape denote the two FIP200NTD monomers in the dimer. Scale bar is 20 nm. (D) Pulldown assays of mutant ATG13MR constructs (M1–M3) and WT with FIP200NTD. Amylose resin was used to pull down purified GST-ATG13MR:FIP200NTD-MBP complex. The pulldown results were visualized by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. (E) Quantification of mito-mKeima ratiometric FACS analysis of HeLa cells stably expressing mito-mKeima–P2A-FRB-Fis1 and FKBP-GFP-ATG13 or mutant after 24 h of Rapalog treatment. n = 3 biological replicates. All values are mean ± SD. P values: *, = < 0.05; ****, < 0.0001. n.s., not significant. a.a., amino acid.