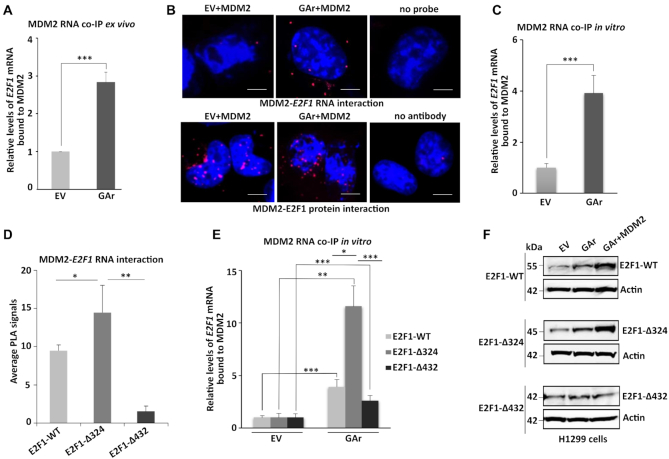
Figure 2.
MDM2 interacts with the E2F1 mRNA during GAr-induced mRNA translation stress. (A) Graph shows the fold enrichment of E2F1 mRNA co-immunoprecipitated with MDM2 (RNA co-IP) from H1299 cell lysates under normal (EV) and mRNA translation stress (GAr) conditions. (B) Proximity ligation assay (PLA) shows the MDM2 protein – E2F1 mRNA interactions (upper panel, red dots) and MDM2 – E2F1 protein-protein interactions (lower panel, red dots) in situ under normal and translation stress conditions in H1299 cells. (C) The graph shows E2F1 mRNA bound to recombinant MDM2. Total mRNA was isolated from H1299 cell lysates expressing EV or the GAr and used for in vitro RNA co-IP with recombinant purified MDM2 protein followed by RT-qPCR against E2F1 mRNA. (D) PLA quantification (average number of dots per cell) of in situ MDM2 – E2F1 mRNA interactions using indicated E2F1-WT, E2F1-Δ324 and E2F1-Δ432 constructs in H1299 cells (see also Supplementary Figure S3). (E) Graph shows relative GAr-dependent enrichment of indicated E2F1 mRNAs bound to recombinant MDM2. (F) WB showing protein levels from indicated E2F1 constructs in H1299 cells expressing the GAr with, or without, over expressing MDM2. Actin was used as a loading control and the WB data shows one of three representative experiments. Statistical significance was calculated using t tests (***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05) of three independent experiments. Scale bars 10 μm.