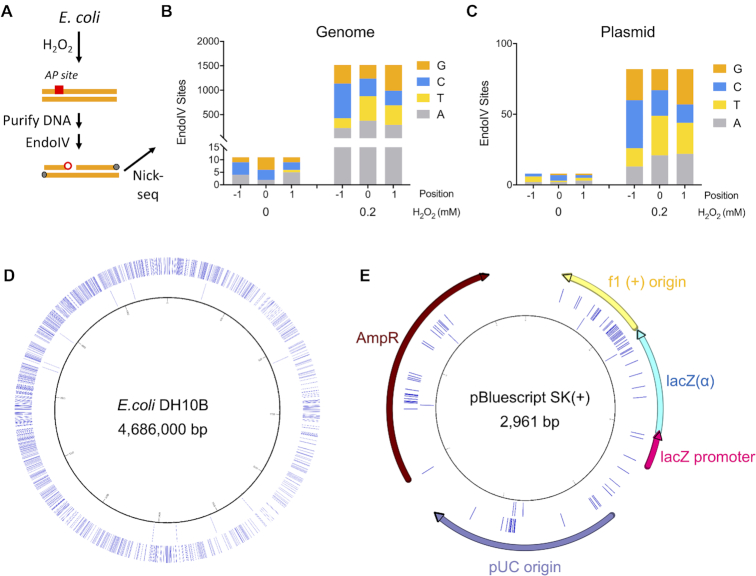
Figure 4.
Application of Nick-seq to quantify abasic sites. (A) generated by H2O2 exposure in E. coli. Cells were treated with a non-lethal dose of H2O2 (0.2 mM) and AP sites in isolated DNA were converted to strand-breaks with EndoIV, followed by Nick-seq mapping. (B) Detection of H2O2-induced EndoIV- sensitive DNA damage sites in E. coli. genomic DNA by Nick-seq. Data for AP sites in the E. coli genome are detailed in Supplementary Table S5. (C) Detection of H2O2-induced EndoIV- sensitive DNA damage sites in a plasmid maintained in this strain of E. coli. Data for AP sites in the E. coli genome are detailed in Supplementary Table S6. (D) The circos plot shows the locations of EndoIV-sensitive sites in E.coli genomic DNA. Outward from the center, circles represent: 0 and 0.2 mM H2O2 induced EndoIV-specific DNA damage sites. (E) The distribution of EndoIV-sensitive sites in the plasmid. Outward from the center, circles represent: 0 and 0.2 mM H2O2 induced EndoIV-specific DNA damage sites.