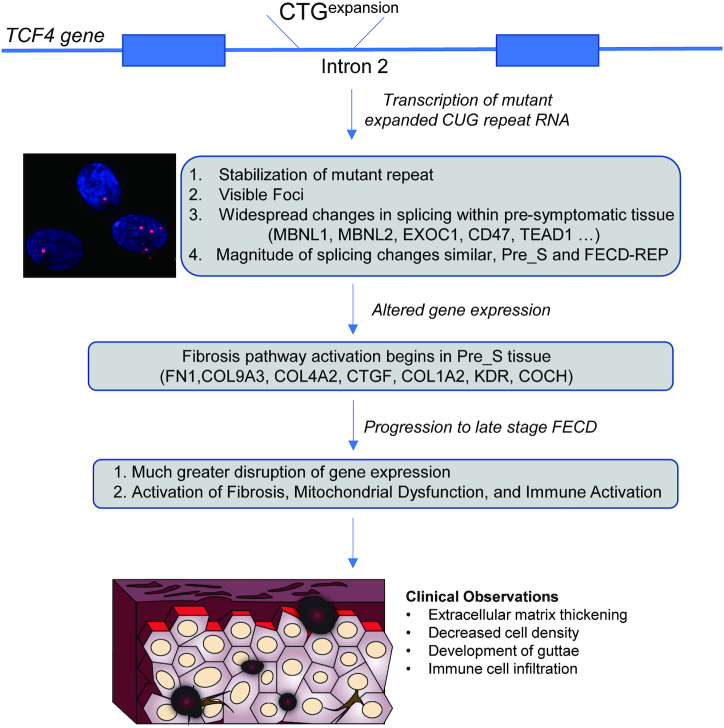
Figure 10.
Schematic diagram of FECD molecular and disease progression from CTG expanded repeat mutation at the TCF4 locus to advanced FECD. Initially, the GTC expansion expresses the CUG repeat RNA. The expanded repeat mutation that causes FECD-REP is a relatively common genetic mutation, making Pre_S tissue available for analysis. While Pre_S tissue appears normal upon clinical observation, foci can be detected, we observe changes in splicing and gene expression, the mutant intronic repeat is stabilized and early signs of fibrosis pathway activation are apparent. In late stage disease, more pronounced changes in splicing and gene expression accompany clinically observable systems and loss of vision.