Figure 4.
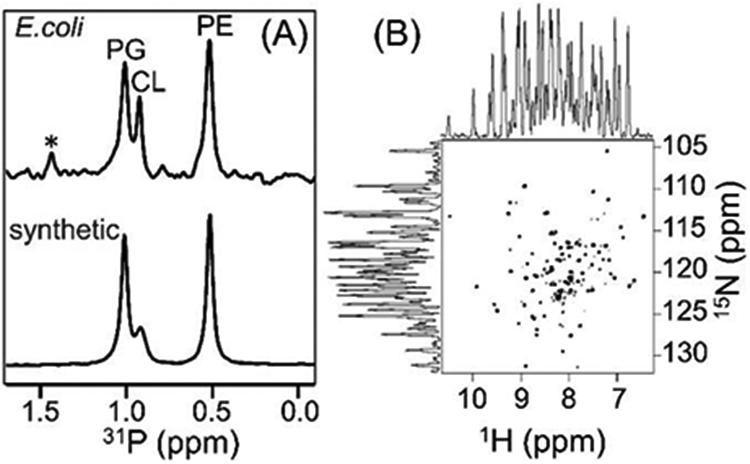
(A) 31P NMR spectra of native E. coli lipids present in the polymer nanodiscs and of the artificially reconstituted synthetic lipids (a reference sample) acquired under by decoupling protons. The protein sample was prepared in 20 mM HEPES buffer pH 7.4 containing 50 mM NaCl and 100 mM sodium cholate. The spectra were recorded using a 500 MHz Bruker NMR spectrometer equipped with a room-temperature 1H/31P/2H BB reverse probe. The synthetic lipids (PE: phosphatidylethanolamine, CL: cardiolipin, and PG: phosphatidylglycerol) were prepared in a PE:CL:PG molar ratio of 7:1.2:4.3. * indicate the uncharacterized E. coli lipids. (B) 2D 1H/15N TROSY-HSQC NMR spectrum of 65 μM 15N-labelled cytochrome-b5 in native nanodiscs. The 1H and 15N line widths were measured to be 27-35 Hz and ~18 Hz, respectively. The protein sample was prepared in 20 mM potassium phosphate buffer pH 7.4, 50 mM NaCl. The 2D NMR spectrum was recorded at 25 °C using a Bruker Avance III 800-MHz spectrometer equipped with a cryogenically cooled triple-resonance probe.
