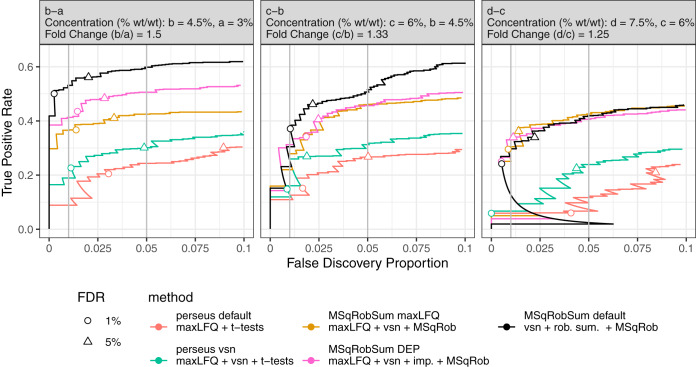
Fig. 3.
Improvements of DE analysis using a modular data analysis workflow. We show incremental improvements in DE analysis by incrementally changing components in the workflow. The data consists of E. Coli proteins spiked at four different concentrations (a, b, c, and d) in a human proteome. The plot shows the performance of each method for the pairwise comparisons b-a, c-b, and d-c (True Positive Rate = E. Coli/(Total E. Coli); False Discovery Proportion = Human/(Human + E. Coli)). The circle and triangle are at 1 and 5% FDR, respectively, as estimated by the method. Perseus default performs t-tests on maxLFQ protein summaries for DE analysis. However, its performance is low and FDR is not controlled. Adding VSN normalization to the protein summaries boosts the performance of the DE analysis (perseus vsn). This workflow is further improved by replacing conventional t-tests by MSqRobSum's inference step (MSqRobSum maxLFQ). Adopting DEP's mixed imputation scheme results in an additional gain in performance (MSqRobSum DEP), whereas the best results are obtained by replacing maxLFQ and mixed imputation with our robust summarization (MSqRobSum default).