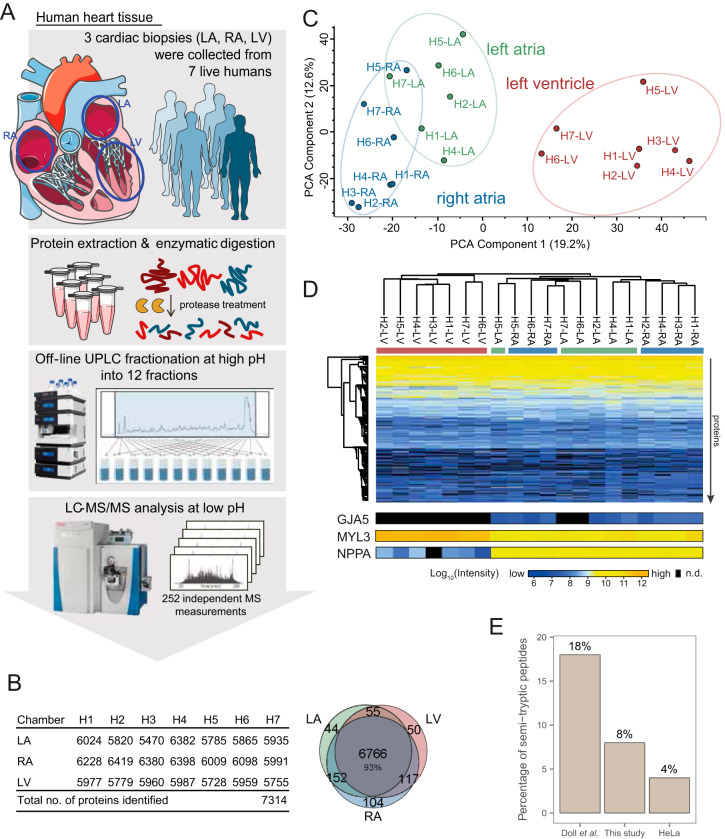
Fig. 1.
In-depth human cardiac proteome across chambers identified 7314 proteins from live tissue biopsies. A, High-resolution LC-MS/MS proteomics workflow for deep proteome measurements of freshly isolated cardiac biopsies from seven live individuals undergoing mitral valve surgery. B, In total 7,314 proteins were identified across left ventricle, right atrium and left atrium from the seven patients (H1-H7). The Venn diagram shows overlap between protein identifications in each chamber (6766 proteins identified in all chambers). C, Principal component analysis (PCA) shows distinction of samples according to chambers, with 19.2% of the variation in the dataset being explained by differences between ventricle and atria along PCA component 1. Separation of right and left atrial samples was observed along components 2 and 4 (12.6%, and 6.8%). D, Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of cardiac proteome samples shows clustering of ventricular and atrial samples (columns) according to protein expression profiles (rows). For three proteins with known chamber-specific expression, protein intensities are displayed at the bottom. E, Extent of unspecific protein degradation evaluated by fraction of semi-tryptic peptides for cardiac samples collected post mortem (7), our cardiac proteomes, and of a HeLa proteome. LA: left atrium, RA: right atrium, LV: left ventricle, UPLC: ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography, MS: mass spectrometry, n.d.: not detected. Data based on biopsy measurements of seven individuals: 7 RA biopsies, 6 LA biopsies, 7 LV biopsies are underlying this analysis.