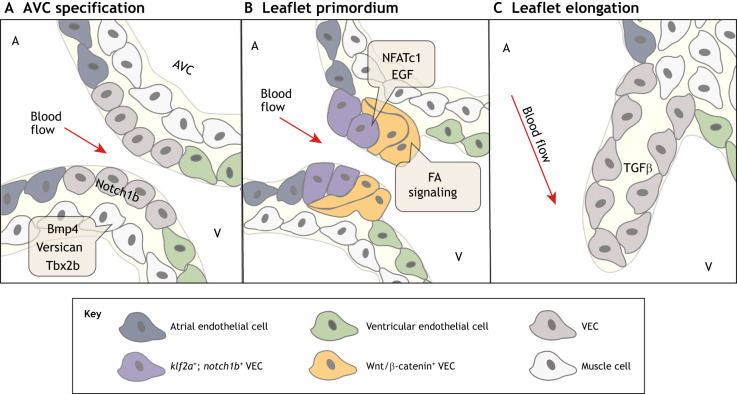
Fig. 5.
Molecular pathways regulating zebrafish valve development. (A) At ∼36-48 hpf, the restriction of bmp4, versican and tbx2 in the myocardium and notch1b in the endocardium initiates atrioventricular canal (AVC) specification between the atrium (A) and the ventricle (V). (B) At ∼50-60 hpf, endocardial cushion-like valve primordia then form through partial endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndoMT), apparent by endocardial invagination and collective migration. klf2a- and notch1b-expressing valve endothelial cell (VEC) progenitors on the ventricular side of the AVC undergo EndoMT or invaginate under notch1b-expressing valve progenitors on the atrial side of the AVC. The NFATc1, Wnt, Notch, EGF and focal adhesion (FA) signaling pathways have also been implicated in the formation of valve primordia. (C) At ∼100 hpf-adult, valve primordia then elongate and thin in response to TGFβ signaling, and remain thin with little extracellular matrix until 28 dpf. The direction of pulsatile blood flow in relation to developing valve structures is indicated (red arrow). hpf, hours post fertilization.