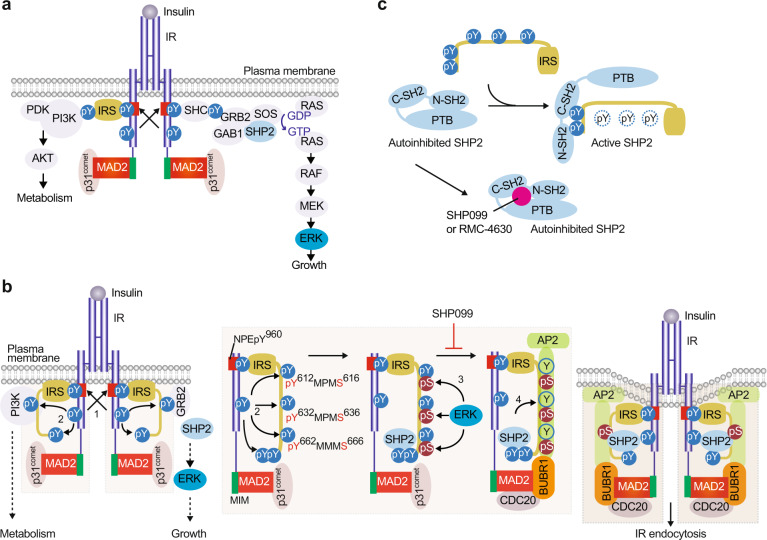
Fig. 1. IRS- and MAD2-dependent mechanisms collaborate to trigger IR endocytosis.
a The insulin receptor signaling pathway. b Model of the regulation of IR endocytosis by IRS and spindle checkpoint proteins. In the basal state, p31comet prevents IR endocytosis. Activated IR auto-phosphorylates multiple tyrosine residues on IR, including Y960 in the NPEY960 motif (1), recruits IRS proteins and initiates insulin signaling cascades. IR phosphorylates Y612/Y632/Y662 of the YXXΦ motifs on IRS1 (2). Activated ERK phosphorylates S616/S636/S666 on IRS1 (3). SHP2 binds to the C-terminal phosphotyrosine sites on IRS1 and dephosphorylates pY612/pY632/pY662 of the doubly phosphorylated IRS1 (pY/pS) to facilitate the IRS1–AP2 interaction (4). IR-bound MAD2 binds to BUBR1-CDC20, providing another binding surface for AP2. These two modules promote IR endocytosis. Inhibition of the feedback regulation prevents IR endocytosis, prolongs metabolic branch of insulin signaling, and improves insulin sensitivity. MIM, MAD2-interacting motif.