Figure 1.
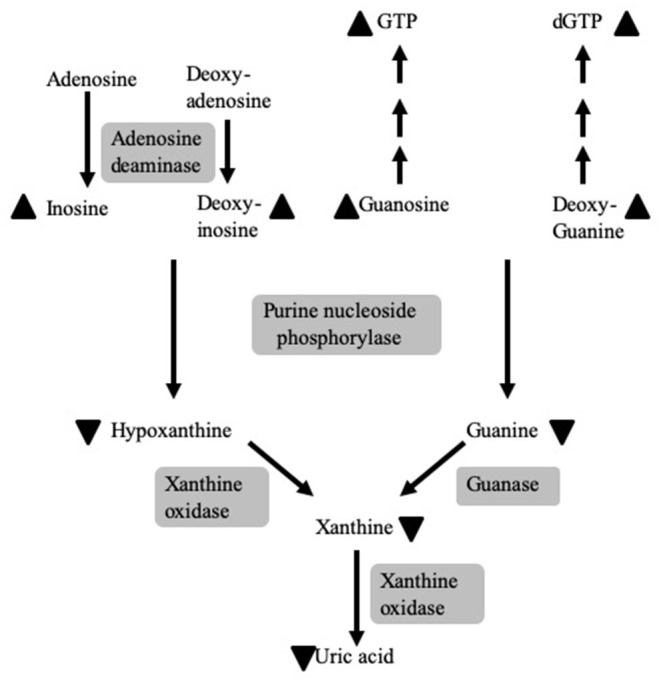
The role of PNP in purine metabolism and the consequences of PNP deficiency. PNP reversibly catalyzes the phosphorolysis of inosine, deoxy-inosine, guanosine, and deoxy-guanosine. PNP deficiency causes the accumulation (depicted by upward pointing arrowheads) of the enzymes' substrates and their phosphorylated derivatives, GTP and dGTP, while preventing the generation (depicted by downward pointing arrowheads) of hypoxanthine, guanine, xanthine, and, subsequently, uric acid. Enzymes are noted by a gray background.
