Fig. 1.
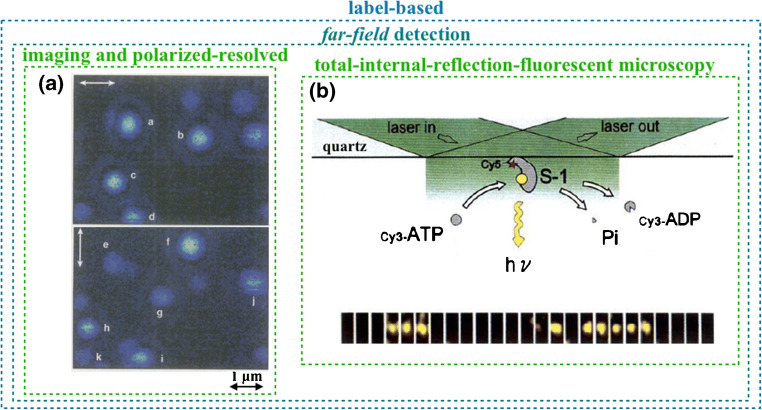
Label-free far-field single-molecule detections. a Sequential fluorescence images (top and bottom panels) of the same sample area showing the fluorescence image from single dye molecule inclusions (marked with letters a–i) in a PMMA film at a PMMA–air interface; images are taken with 532-nm laser excitation polarized as indicated by the white arrows. (Reprinted with permission from Ref. [4] Copyright 1996 Science). b The top panel shows a representation of the total internal reflection fluorescent microscopy principle for a single myosin subfragment (S-1; recognition element) that selectively binds adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP hydrolysis generates adenosine diphosphate (ADP) plus a phosphate (Pi) yielding energy; the bottom panel shows the measurement of an individual fluorescently labeled ATP molecule during the elicited turnover reaction. The ATP is seen only when in the proximity of the quartz interface. (Reproduced with permission from Ref. [5] Copyright 1995 Springer Nature)