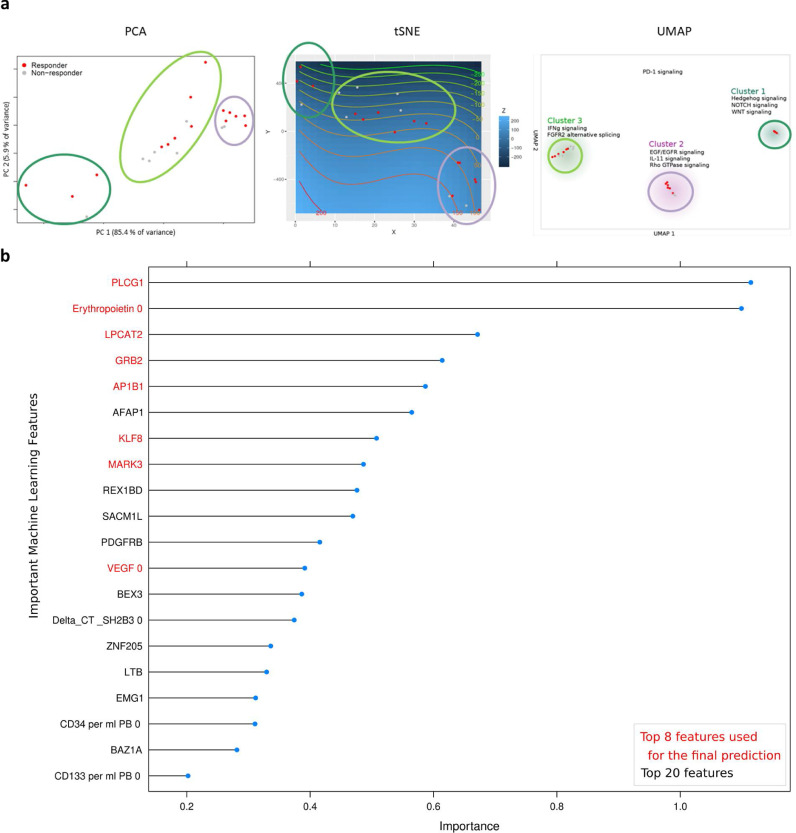
Fig. 2.
a: ML subgroup clusters of cohort study (Responder, n=14, red points; Non-responder, n=9, grey points). b: Machine learning feature selection on clinical trial research data and RNA-Seq data. Accuracy comparison for the supervised prediction of the patient responsiveness using only preoperative data. Results are obtained after feature selection and subsequent prediction with two independent classifiers. The graph shows the true positive prediction weights of the ML model (RF for feature selection and SVM for final prediction). Combinations and subsets of these features have been subsequently used to train the final model. The importance indicates a hierarchy of the most relevant features needed for a classification.