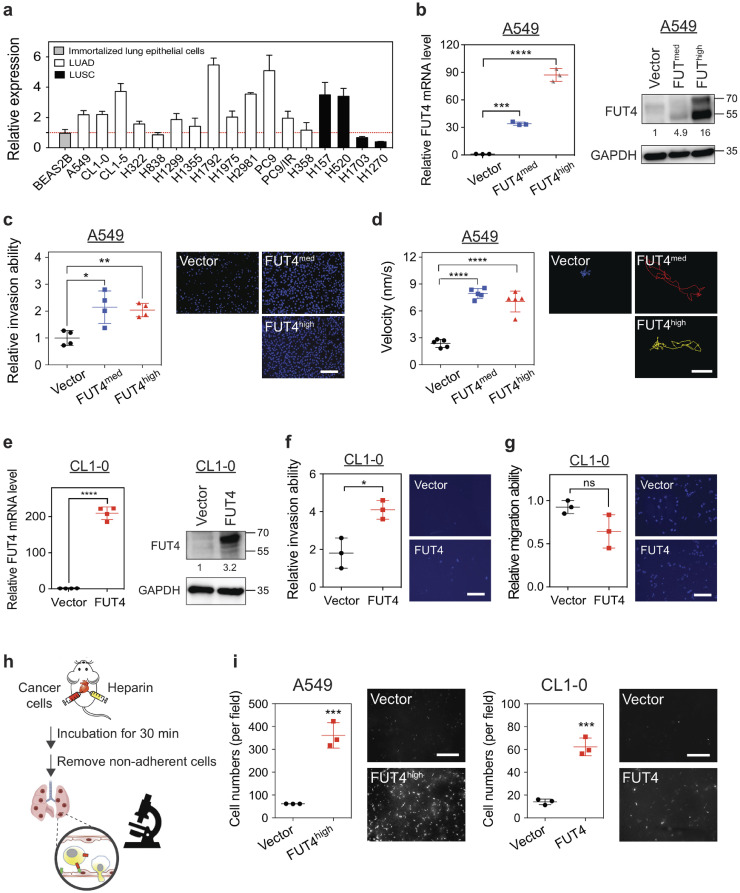
Fig. 2.
FUT4 promotes aggressive phenotypes of human lung cancer cells. (a) FUT4 mRNA expressions in various human lung cancer cell lines analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR. All experiments were performed in triplicates and presented as mean ± SEM. LUAD: adenocarcinoma. LUSC: squamous cell carcinoma. (b) FUT4 mRNA (left panel) and protein levels (right panel) in A549 human lung cancer cells transduced with FUT4 (A549_vector, A549_FUT4med, A549_FUT4high) measured by quantitative real-time PCR and western blots. (c) Dot plots showing relative invasion ability of A549 cells measured by matrigel-based transwell invasion assays. Representative images of cells with DAPI nuclear stains in the lower chambers are shown in the right panels. Relative invasion ability was calculated using the cell number in the lower chamber of the transwell system for each clone compared to that of the vector control. (d) Dot plots showing migration velocity of A549 cells measured by single-cell tracking assays under a fluorescence microscope. Data were analyzed using Metamorph® software. The paths of cell migration were delineated in the right panels using pseudo-colors. (e) FUT4 mRNA (left panel) and protein levels (right panel) in CL1–0 human lung cancer cells overexpressed with FUT4 (CL1–0_vector, CL1–0_FUT4) measured by quantitative real-time PCR and western blots. (f) Dot plots showing relative invasion ability of CL1–0 cells measured by matrigel-based transwell invasion assays. Representative images of cells with DAPI nuclear stains in the lower chambers are shown in the right panels. Relative invasion ability was calculated using the cell number in the lower chamber of the transwell system for each clone compared to that of the vector control. (g) Dot plots showing the migration ability of CL1–0 cells measured by transwell migration assays. Relative migration ability was calculated using the cell number in the lower chamber of the transwell system for each sample compared to that of the vector control. (h) Diagram of in vivo extravasation and lung colonization assay following injection of lung cancer cells into the right ventricle of C57BL/6 mice. Mice were sacrificed 30 mins after intracardial injection. Whole lung perfusion with normal saline was performed to remove blood and cells not adhered to the pulmonary vasculature. (i) Numbers of lung cancer cells with FUT4 over-expression (left panel, A549_FUT4high; right panel, CL1–0_FUT4) adhered to the vascular walls or retained in the lung tissues following intracardial injection were visualized under Zeiss Axio Observer microscope.
Scale bar in c, d, f, and g; 100 μm. Scale bar in i ; 1 mm. p value in (b-d) was calculated by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's test, and in (e, f, g, and i) was by Mann-Whitney test. All experiments were performed in three biological replicates and presented as mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001. ns: not significant.