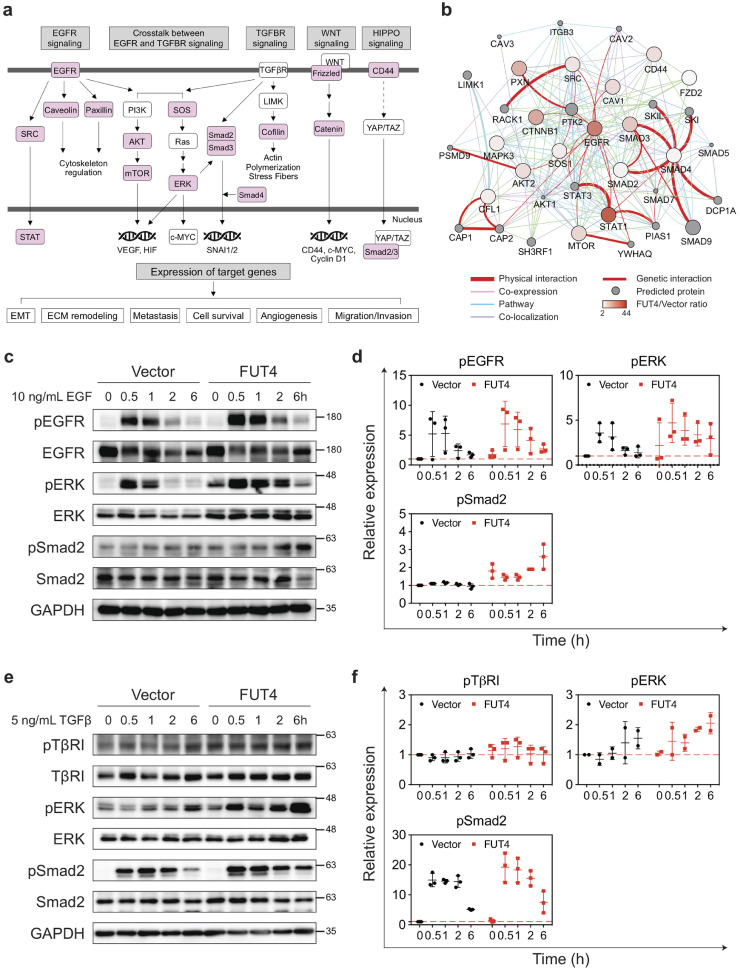
Fig. 6.
FUT4 enhances metastasis-related signaling via the fucosylation of cascade proteins. (a) Immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-Lex antibody followed by tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) in A549_FUT4high and CL1–0_FUT4 cells reveals key mediator proteins (in pink) in oncogenic signaling cascades including EGF, TGFβ, WNT and HIPPO pathways. (b) Protein networks showing protein-protein interactions between FUT4 acceptor proteins bearing higher levels of Lex antigens in A549_FUT4high cells relative to A549_vector cells. The data were analyzed by Cytoscape (ver. 3.6.1) using the GeneMania application (ver. 3.4.1). (c) Western blot analyses of signaling cascade proteins in the EGFR pathway in A549_FUT4highversus A549_vector cells at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, and 6 hrs following the addition of 10 ng/mL EGF. (d) Quantifications of signal intensities in (c) for phospho-EGFR, phospho-ERK, and phospho-Smad2 from three biological replicates. (e) Western blot analyses of signaling cascade proteins in the TGFβ signaling pathway in A549_FUT4highversus A549_vector cells at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, and 6 hrs following the addition of 5 ng/mL TGFβ. (f) Quantifications of signal intensities in (e) for phospho-TGFβ receptor I, phospho-ERK, and phospho-Smad2 from three biological replicates. p value in (d, f) was calculated by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. ns: not significant. All experiments were performed in three biological replicates and presented as mean ± SEM.