Fig. 1.
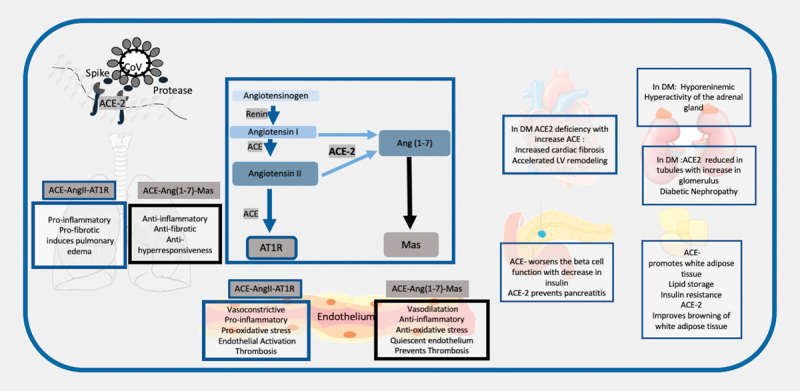
Schematic Representation to show the renin angiotensin system in diabetes and the interaction of the SARS-CoV 2 with the ACE-2. 1. The SARS-CoV 2 interacts with the ACE-2 through the spike proteins after priming by tissue serene proteases. It uses the ACE-2 protein to enter the alveolar cells in the lungs. 2. The renin angiotensin system consists of renin which catalyzes the conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin 1 (Ang 1). The subsequent axis depends on the balance between the Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) and ACE-2. ACE converts Ang 1 to Ang II and this acts in the angiotensin receptor (AT 1 R), whereas ACE-2 converts it to Ang-(1–7), which acts on the Mas receptor. 3. In the respiratory system activation of ACE leads to a proinflammatory, pro-fibrotic , pro-hyperresponsiveness response in the respiratory system, whereas ACE-2-Ang-(1–7)-Mas induces a protective mechanism of anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic and anti-hyperresponsiveness. A lower ACE-2 will put these individuals at higher risk of respiratory distress. 4. In hypertension, diabetes, and CVD, the ACE related pathway is activated with downregulation of the ACE-2 pathway. These results in the multi-organ complications seen in metabolic diseases with endothelial dysfunction promoting atherosclerosis, increased cardiac fibrosis and LV remodeling, diabetic nephropathy, hyperactivity of adrenal gland, and it decreases insulin release and increases insulin resistance. 5. Infection with COVID-19 may exacerbate the ACE-2 deficiency in these patients in all organs and maybe responsible for the multiorgan failure.
